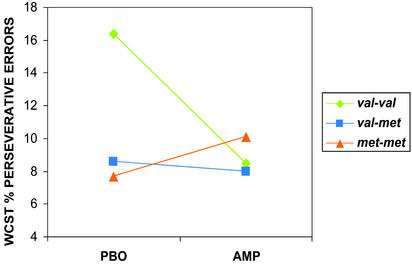
Figure 3.
WCST percent perseverative errors on AMP and PBO showing a significant drug × genotype interaction (matched groups; ANOVA F(2,14) = 5.2, P < 0.02). Note that individuals with the val/val genotype perform better on AMP (fewer errors), whereas individuals the met/met genotype get worse (more errors) and individuals with the val/met genotype show no discernable effect on performance. Analysis of data from all subjects (val/val = 10, val/met = 10, and met/met = 6) who performed the task revealed a similar drug × genotype interaction (ANOVA F(2,23) = 3.7, P < 0.04). In addition, analysis using percent total errors (perseverative and nonperseverative errors; a measure of general performance) also revealed a significant drug × genotype interaction (ANOVA F(2,22) = 4.3, P < 0.02). Subjects with the val/val genotype showed better overall performance scores (i.e., percent fewer total errors) on AMP, whereas subjects with the met/met genotype showed the opposite response. In essence, this suggests that, although the val/val subjects on PBO made more total errors than they did on AMP, and met/met subjects on AMP made more total errors than on PBO, perseverative errors made up a major portion of the total errors. Thus, AMP did not induce perseverative errors independent of genotype.