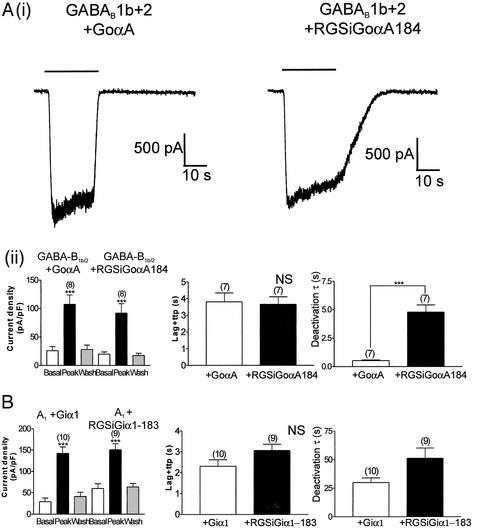
Figure 6.
Effects of RGS-insensitive GoαA on channel kinetics in response to GABA-B1b/2 receptor stimulation. (Ai) Examples of current traces recorded from HKIR3.1/3.2/GGB cells transiently transfected with either GoαA (Left) or RGSiGoαA (Right). Baclofen (100 μM) was applied for 20 s as indicated. (Aii) Mean data obtained from these experiments. Current densities are shown (Left). Current density was measured at −60 mV before (basal), during (peak), and after (wash) application of 100 μM baclofen for 20 s in the HKIR3.1/3.2/GGB cell line transiently expressing either the PTx-resistant GoαA or the RGS-insensitive, PTx-resistant GoαA (RGSiGoαA). Channel activation (Center) and deactivation (Right) kinetics are shown. We saw no significant difference in channel activation between GoαA and RGSiGoαA (P > 0.05), whereas deactivation via the RGS-insensitive G protein was dramatically slower than GoαA (P < 0.001). (B) Summary of data from similar experiments with the HKIR3.1/3.2/A1 cell line and transiently expressing either Giα1C351G or RGSiGiα1. (Left) Current densities were comparable in both groups, but no significant differences were seen between the PTx-resistant Giα1 and RGSiGiα1 in terms of channel activation and deactivation. ttp, time to peak.