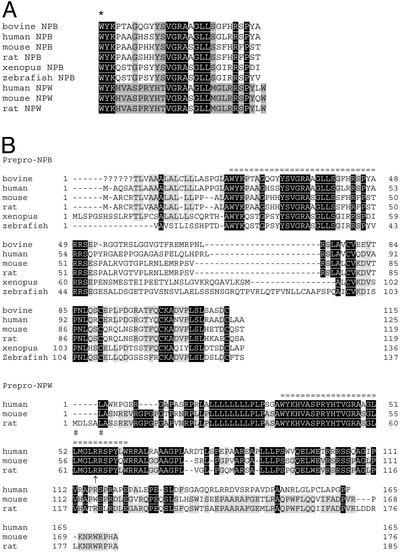
Figure 1.
Amino acid sequences of NPB and NPW. (A) Amino acid sequences of mature NPB and NPW peptides. An asterisk indicates the posttranslational bromination site of the native bovine NPB. Peptide sequences of other species are deduced from cDNA sequences. Amino acid identities between NPB and NPW are shown in black. Shaded residues are conserved only within the NPB or NPW. (B) Deduced amino acid sequences of prepro-NPB and NPW precursor polypeptides. Mature peptides are marked by equal signs. Question marks indicate undetermined sequence of bovine prepro-NPB. Human and mouse prepro-NPW cDNA do not have a translation initiator ATG codon; putative translation initiation sites are indicated by a pound sign. An arrow indicates a possible additional processing site for NPW. Identical amino acids within the orthologues are shown in black. Lightly shaded residues are conserved in more than four of six (NPB) or two of three (NPW) species.