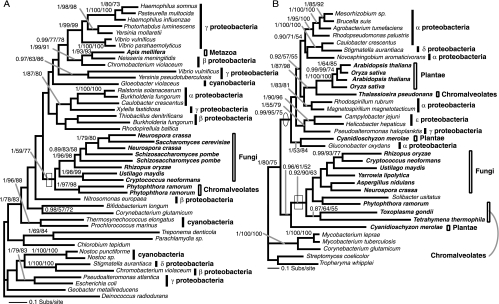
FIG. 1.
Phylogeny of DAHP I and DAHP II genes. (A) Phylogeny of DAHP I gene, calculated from an amino acid alignment of 45 sequences and 327 characters. The node demonstrating oomycete and fungal monophyly is shown with a box. (B) Phylogeny of DAHP II, calculated from an amino acid alignment of 35 sequences and 372 characters. The node demonstrating the monophyly of arom possessing taxa and the putative HGT with S. usitatus is shown with a box; the node showing separation of the land plants/diatom from the other eukaryotes is circled. This node also represents the best support for a putative HGT between Plantae and a proteobacterium. The topologies shown are the results of the Bayesian topology search arbitrarily rooted on a eubacterial branch. Topology support values for this and all subsequent phylogeny figures are illustrated when both bootstrap results were above 49% and are shown in the order Bayesian posterior probability/% 1,000 ML distance bootstraps/% 100 fast ML-PHYML bootstraps. A selection of eubacteria and the eukaryotes are labeled according to higher taxonomic classification (prokaryote taxa using line bars and eukaryotes using box bars). In addition, the eukaryotes are named in bold. These labeling conventions are also used in all subsequent figures.