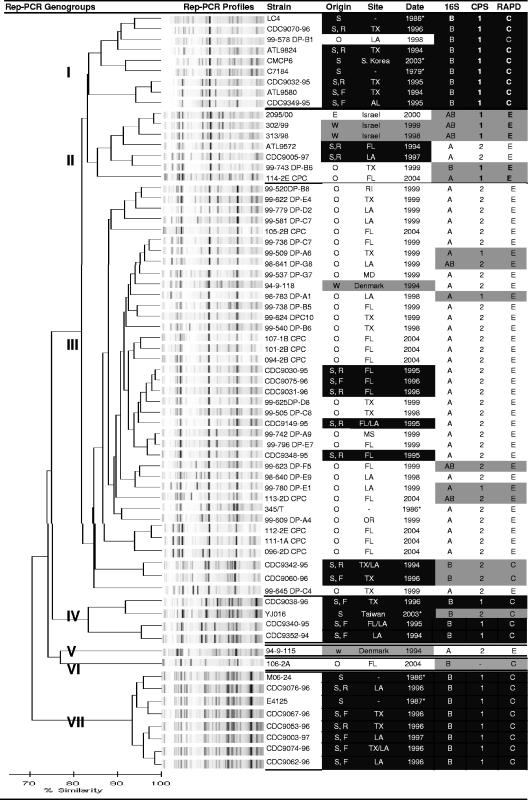
FIG. 1.
Comparison of rep-PCR analysis and genotype profiles for clinical and environmental strains of V. vulnificus. A scale for rep-PCR similarity is shown at the bottom of the figure. Strain sources are described in detail in the text, and a description of strains in the table includes the following: S, septicemia from oyster consumption; W, wound infection; O, oyster; E, environmental, not oyster; F, fatal outcome of infection; R, recovered from infection. Strains from septicemia origins are shaded in black, wound infection isolates are shaded in gray, and environmental isolates are not shaded. Where available, information on the site and date of isolation of strains is provided; alternatively, the date that the strains first appeared in publication is shown (asterisk). Specific genotype profiles were determined by PCR as described in the text and included the following: 16S rRNA gene (type A, B, or A+B), group 1 CPS genes (alleles 1 and 2; a dash is used to indicate where CPS primers did not amplify), and RAPD-associated locus (C type and E type). Typical “clinical” profiles (16S B, CPS allele 1, and RAPD C type) are shaded in black, “environmental” profiles (16S A or A+B, CPS allele 2 or CPS negative, and RAPD E type) are not shaded, and atypical combinations are shaded in gray.