Figure 3.
Positional Cloning of the ETA3 Locus.
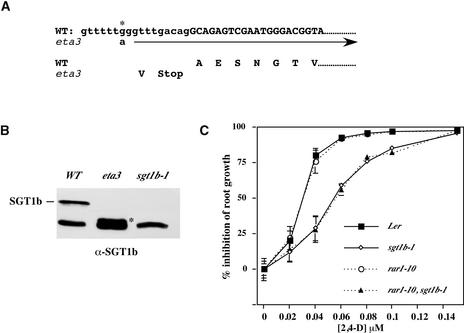
(A) Sequencing of a reverse transcriptase–mediated PCR product revealed that the eta3 mutation causes a G→A substitution (asterisk) near the splice acceptor site of the final exon. This substitution creates a false splice acceptor site and the inclusion of the intron sequence AGGTTTGACAG in the eta3 mRNA, resulting in a premature termination codon. Lowercase and uppercase letters indicate intron and exon sequences, respectively.
(B) Protein gel blot analysis of the ETA3/SGT1b protein. The position of the truncated eta3 protein is marked with the asterisk in lane 2. The bottom-most band represents an unknown cross-reacting protein.
(C) Root growth assay with Landsberg erecta (Ler), sgt1b-1, rar1-10, and sgt1b-1 rar1-10 seedlings. Error bars indicate standard deviations from the mean.