FIG. 3.
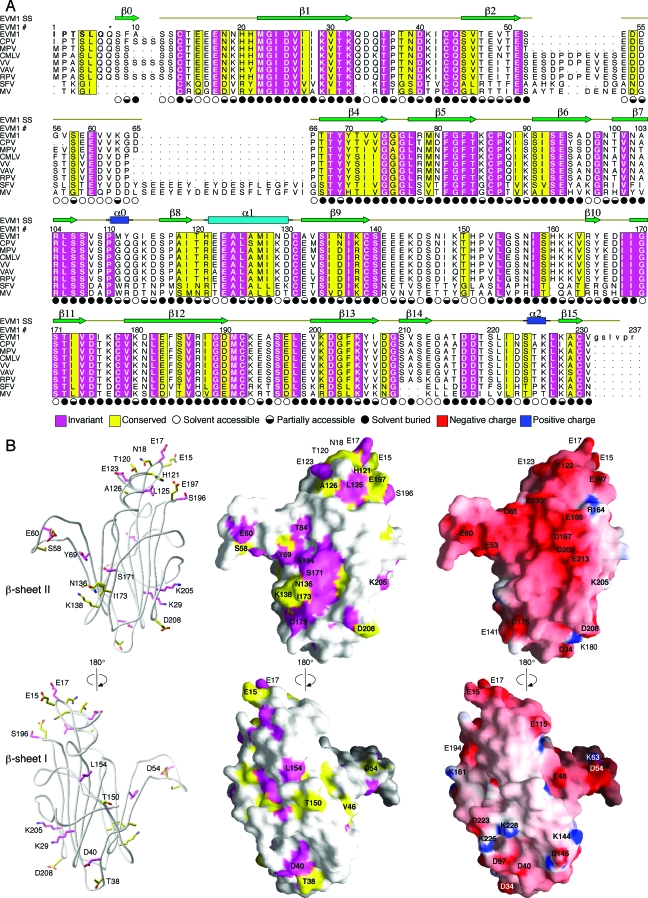
Sequence conservation can be used to predict the chemokine binding site on EVM1. (A) The sequence of EVM1 is aligned with eight other members of this chemokine binding protein family from other poxviruses. CPV, cowpox; MPV, monkeypox; CMLV, camelpox; VAV, variola virus; RPV, rabbitpox virus; SFV, Shope fibroma virus. The secondary structure of EVM1 is shown above the alignment. Regions of sequence conservation are highlighted. Magenta, invariant residues; yellow, residues with a conservation index of 7 or greater as determined by ALSCRIPT (5). Symbols indicating the solvent accessibility of each side chain are shown under the alignment. Filled circles, <30% accessible; half-filled circles, 30 to 60% accessible; open circles, >60% accessible. The asterisk above residue 7 indicates the position of the first residue of the molecule, a pyroglutamate, when the second signal peptide cleavage site is used. (B) Ribbon diagram (left) highlights the conserved, surface-exposed side chains suggesting a potential binding site. Sequence conservation is mapped to the EVM1 surface (middle). Electrostatic surface potential of EVM1 as calculated by GRASP (29) is mapped to the surface (right). Surface colors are contoured from red (−15 kT) to blue (15 kT).