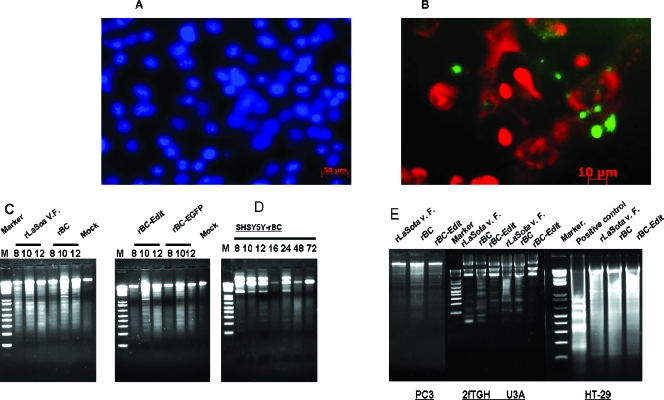
FIG. 2.
Morphological features of apoptosis in rNDV-infected human tumor cells. Cells were either mock infected or infected with rLaSota V.F., rBC, rBC-Edit, or rBC-EGFP strains of NDV at an MOI of 0.01. At 6 and 14 h postinfection, apoptotic cell death was visualized by staining the infected cells with DAPI (1 μg/ml). (A) Condensation of chromatin and nuclear fragmentation of rNDV-infected HuTu80 cells. (B) Fluorescein isothiocyanate-annexin V (10 mg/ml) staining of NDV-infected HuTu80 cells. (B) Phosphatidyl serine externalization to the outer leaflet of the infected cell membrane is evident by green fluorescence of the cell membrane. (C) DNA laddering of infected cells was examined by using an apoptotic DNA laddering kit (Roche) per the manufacturer's instructions. Intranucleosomal DNA fragmentation is evident as a laddering pattern of the cellular DNA in rNDV-infected HuTu80 cells at 8, 10, and 12 h postinfection. (D) DNA laddering of SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells at 8, 10, and 12 h postinfection. (E) DNA laddering of rNDV-infected PC3, 2fTGH, U3A, and HT29 cells at 12 h postinfection.