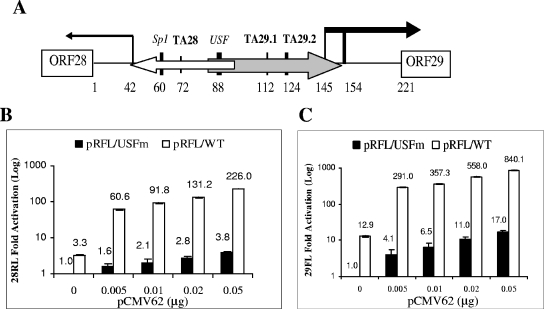
FIG. 2.
Synergistic IE62-USF activation of the VZV ORF28/29 regulatory element. (A) Schematic of the VZV ORF28/29 regulatory element showing authenticated transcription factor binding sites and TATA elements. The locations of the two overlapping minimal promoters are shown as open (ORF28) and gray (ORF29) arrows, respectively. The difference in thickness reflects their levels of transcription efficiency in the presence of IE62. The vertical lines capped by an arrow indicate the positions of transcription start sites. The difference in thickness of the two bold vertical lines over the ORF29 gene transcription start sites indicates that one is preferentially utilized (55). (B) Results of transfection experiments showing expression of Renilla luciferase (ORF28 position) activity from the wild-type (open bars) and mutant USFm (solid bars) dual luciferase reporter plasmids in the presence of increasing amounts of the pCMV62 expression plasmid. The level of Renilla luciferase activity observed with the pRFL/USFm reporter in the absence of IE62 was normalized to 1. (C) Results of transfection experiments showing expression of firefly luciferase (ORF29 position) activity from the wild-type (open bars) and USFm (solid bars) dual luciferase reporter plasmids in the presence of increasing amounts of the pCMV62 expression plasmid. The level of firefly luciferase activity observed with the pRFL/USFm reporter in the absence of IE62 was normalized to 1. Luciferase assay data in panels B and C represent the averages of triplicate transfections. The average values are shown above each bar, and the error bars represent standard deviations.