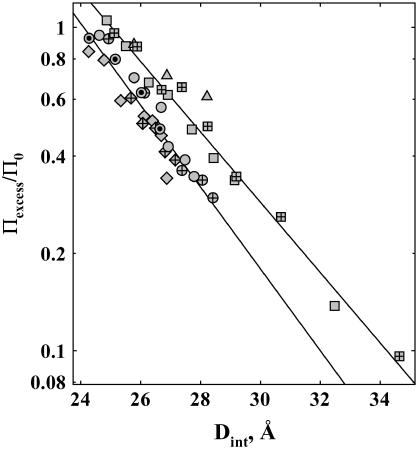
FIGURE 2.
Distance dependence of the change in excess water that excludes MPD. The apparent excess pressure applied by MPD (Eq. 4) normalized by the total MPD osmotic pressure in the bathing solution is shown as dependent on the interhelical spacing. From Eqs. 3 and 5, Πexcess/Π0 = −dΓw/dV, where Γw is the excess water associated with the DNA phase. MPD exclusion is shown for DNA arrays equilibrated against 1.2 M NaBr (squares), 20 mM NaBr (triangles), 2 mM SpdCl3 (circles), and 2 mM Co(NH3)6Cl3 (diamonds). The MPD concentration for the solid symbols was 1 molal, 0.5 molal for the symbols with inner crosses, and 2 molal for symbols with inner dots. The different MPD concentrations overlap for each salt condition, within experimental error, indicating that ΔΓw is independent of solute concentration at any fixed spacing. To a good first order approximation, excess water varies exponentially with the distance between helices. This is illustrated by the linear fits on the logarithmic scale (solid lines) to the NaBr and trivalent ion data.