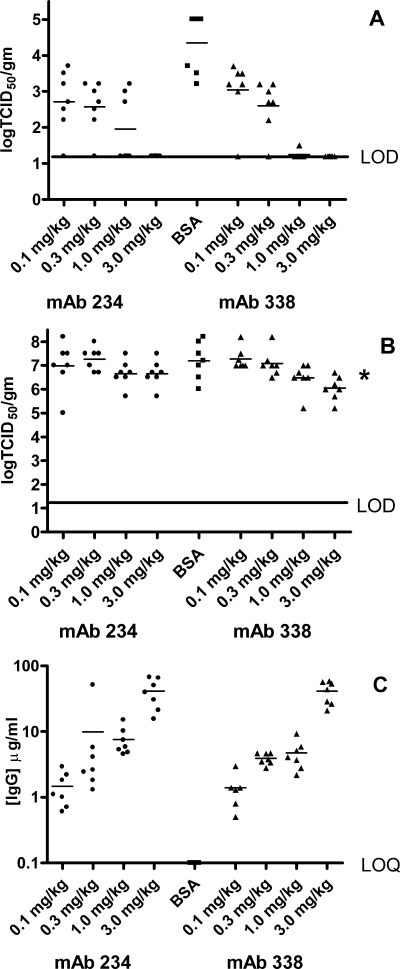
FIG. 2.
In vivo protection against NL100 challenge. Golden Syrian hamsters were injected 24 h prior to intranasal challenge with NL100 with different does of MAb 234 (solid circles), MAb 338 (solid triangles), or with BSA (solid squares). Animals were bled prior to challenge to determine the levels of serum antibodies present at time of challenge. At 4 days postinfection, lungs (panel A) and nasal turbinates (panel B) were harvested, and virus titers were determined as described in Materials and Methods. The limit of detection (LOD) for the viral titers was 1.2 log/g tissue. For MAb quantification, animal serum samples were diluted 1:100 and 1:500 (panel C). The limit of the quantitation (LOQ) for this assay as performed was 0.1 μg MAb/ml serum. P values for MAb 234 were <0.0001, 0.0004, 0.0013, and 0.0042 for doses of 3 mg/kg, 1 mg/kg, 0.3 mg/kg, and 0.1 mg/kg, respectively. P values for MAb 338 were <0.0001, <0.0001, 0.0014, and 0.0145 for doses of 3.0 mg/kg, 1.0 mg/kg, 0.3 mg/kg, and 0.1 mg/kg, respectively. The nasal turbinate P value, indicated by an asterisk, was 0.008. IgG, immunoglobulin G.