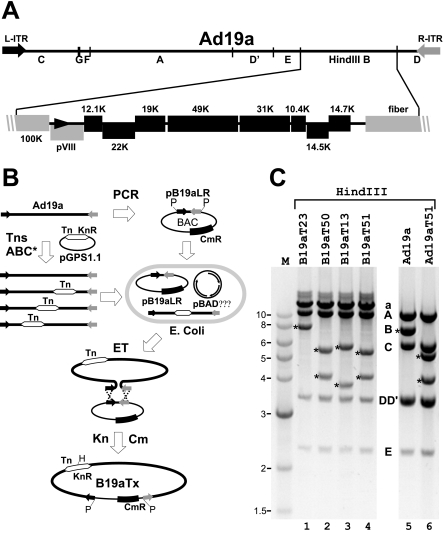
FIG. 2.
Tn-assisted cloning of the Ad19a genome. (A) Schematic representation of the Ad19a genome. The linear Ad genome is flanked by 135-bp ITRs (L-ITR, R-ITR; black and gray arrows). The HindIII fragments are marked according to size from A to G, with the HindIII B fragment shown in greater detail. Nonessential E3 ORFs are shown as black boxes and adjacent essential genes (100K, pVIII, fiber) as gray boxes. Numbers above or below the boxes indicate the names of the E3 ORFs based on their calculated molecular weights. (B) Schematic representation of Tn-assisted cloning of the Ad19a genome. The PCR-amplified Ad19a ITRs were cloned into the BAC vector pKSO carrying a chloramphenicol resistance gene (CmR), thereby generating pB19aLR with PacI (P) sites at each ITR-vector border. This entry vector was introduced into E. coli DH10B together with the recombination plasmid pBADαβγ expressing the respective λ genes involved in recombination. Purified Ad19a DNA was labeled in vitro with a Tn (white double arrows) carrying a kanamycin resistance (KnR) gene by use of TnsABC* transposase and the Tn donor plasmid pGPS1.1. Upon transformation with the Tn-labeled Ad19a DNA, ET recombination (ET) with p19aLR was induced and Ad19a-containing recombinant BACs (B19aTx) were selected by Kn and Cm. For simplicity, the HindIII site (H) present in the Tn is only shown in B19aTx. (C) HindIII digests of BAC DNA from selected Tn-positive clones (B19aT23, B19aT50, B19aT13, and B19aT51; lanes 1 to 4) and viral DNA from wt Ad19a and B19aT51-derived reconstituted virus, Ad19aT51 (lanes 5 and 6). The typical Ad19a HindIII fragments are indicated with the letters A to E (lane 5; F and G are not visible). Fragment A, one of the doublet DD′, and fragment E are visualized in all selected BAC clones. Fragment C and the other DD′ fragment are missing due to their linkage to the vector backbone. Together, these form fragment a. Insertion of the Tn in fragment B introduces an additional HindIII site, yielding two new fragments (marked by asterisks). For B19aT23 the second HindIII B-derived fragment is too small to be visible in this gel. Ad19aT51 was reconstituted by transfection of PacI-cleaved B19aT51 BAC DNA into 293 cells. PacI cleavage removes the plasmid vector; hence, viral DNA lacks fragment a and exhibits the normal end fragments (C and one of the DD′ fragments; compare lanes 5 and 6). Please note the presence of the same two extra fragments derived from fragment B (asterisk) in the recombinant Ad19aT51 virus as in the parental B19aT51 BAC (compare lanes 4 and 6).