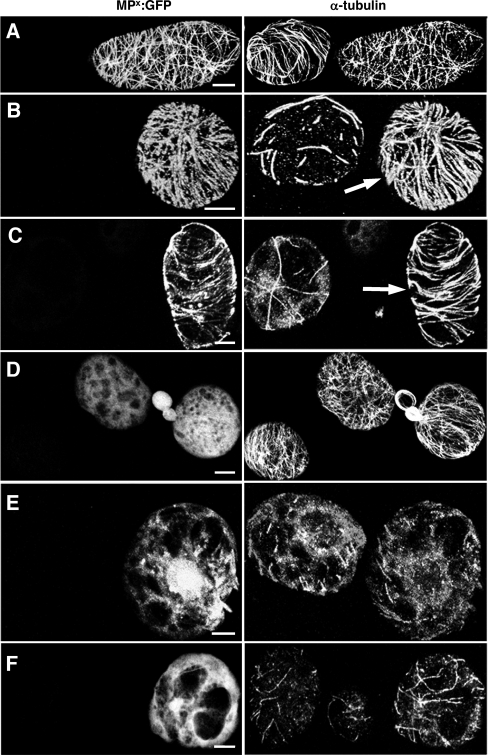
FIG. 2.
MP stabilizes microtubules in BY-2 protoplasts. BY-2 protoplasts infected with TMV derivatives expressing functional or nonfunctional MPs were treated for 1 h with either 50 μM APM or 10 μM oryzalin and subsequently stained with anti-α-tubulin antibody. (A to C) BY-2 protoplasts infected with TMV-MP-GFP. (A) In the absence of microtubule-disrupting drugs, functional MP-GFP colocalizes with microtubules. (B and C) In nontransfected cells treated with APM (B) or oryzalin (C), microtubules are almost completely abolished. In cells infected with TMV-MP-GFP (arrows) treated under the same conditions, a high number of microtubules remain associated with MP-GFP. (D to F) BY-2 protoplasts infected with TMV-MPP81S-GFP. (D) Nonfunctional MPP81S-GFP is diffusely distributed throughout the cytoplasm in the absence of microtubule-disrupting drugs. (E and F) In nontransfected cells, treatment with APM (E) or oryzalin (F) leads to a dramatic disruption of microtubules. Under the same conditions, a similar loss of microtubules is apparent in cells expressing MPP81S-GFP, indicating that the microtubule association of MP is required for microtubule stabilization against these drugs. Bar, 5 μm (A to D and F) and 10 μm (E).