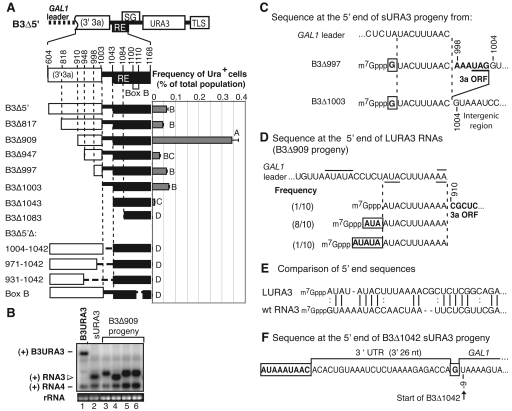
FIG. 6.
Formation of sURA3 RNAs from B3Δ5′. (A) Deletions of B3Δ5′. Nucleotide numbers correspond to the wt BMV RNA3 sequence. The number included in the name of each construct indicates the last nucleotide removed. In internal deletions of B3Δ5′, the nucleotides removed are indicated after the Δ. RNAs were transcribed in vivo from the GAL1 promoter, and the GAL1 mRNA leader was present, as on B3Δ5′. The histogram shows the frequency of Ura+ cells after transcription of each construct for 72 h (9 to 10 yeast generations) in the presence of BMV replication proteins 1a and 2apol. Bars show the averages and standard errors of results from six independent repetitions. Bars with the same letter are not statistically significant. Letter D indicates constructs for which no Ura+ cells were detected. (B) Sample Northern blot of cells that acquired a Ura+ phenotype after transient induction of B3Δ909. Positive-strand RNAs were detected with a 32P-labeled probe against URA3. The B3Δ909 progeny consisted of two sizes (open arrowhead): small replicons that comigrated with sURA3 RNAs (lane 4), and RNAs longer than sURA3 (LURA3, lanes 3, 5, and 6). The bottom panel shows ethidium bromide staining of 18S rRNA. (C) 5′ sequence of representative sURA3 RNAs derived from B3Δ997 and B3Δ1003. Both sURA3 RNAs represent 5′ truncations of the initial plasmid transcript, retaining the last 9 nt of the GAL1 mRNA leader (indicated between vertical dashed lines) and bearing a single noncontiguous 5′ G (boxed). GAL1 leader sequences were fused to B3Δ997 sequences from the 3a ORF (bold) or to RNA3 intergenic region in B3Δ1003. Sequence numbering corresponds to wt RNA3. (D) 5′ sequence of three LURA3 RNAs sequences derived from B3Δ909 and their prevalence among 10 independent LURA3 cDNA clones sequenced. All are 5′-truncated derivatives of the parental B3Δ909 transcript, including the last 9 to 10 nt of the GAL1 leader (indicated between vertical dashed lines). An AA linker generated in cloning is over- and underlined. All downstream RNA3 sequences are in boldface type. In two cases, these sequences are fused at the 5′ end to noncontiguous AU repeats (boxed), which might have been derived by duplication of flanking downstream sequences (underlined) or recombinational joining of upstream sequences (overlined). (E) Comparison of the 5′ end of the most prevalent LURA3 sequence from panel B to the 5′ end of wt RNA3. (F) Representative sequence of a sURA3 RNA derived from B3Δ1042. Such sURA3 RNAs contained the complete sequence of the starting B3Δ1042 transcript, initiated at a previously documented (17) alternate start site 9 nt upstream of the usually cited GAL1 transcription start, fused via a single noncontiguous G (boxed) to the last 26 nt of B3Δ1042, which corresponds to the last 26 nt of the 3′ UTR of wt RNA3, and preceded by 1 to 17 nt of A-rich sequence of unknown origin (boxed).