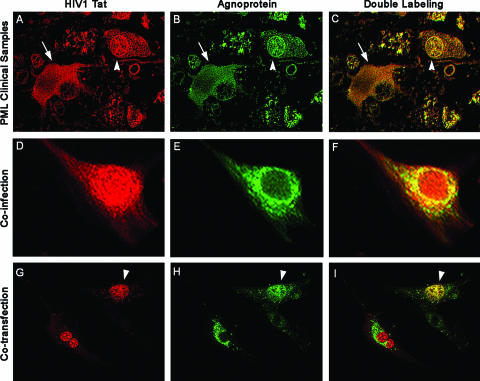
FIG. 1.
Colocalization of HIV-1 Tat and JCV agnoprotein in astrocytes. (A to C) Immunofluorescence for the HIV-1 transactivator protein Tat demonstrates robust expression in the cytoplasm and weaker expression in the nuclear compartment of bizarre astrocytes within demyelinated plaques in a case of AIDS-related PML (A; rhodamine). The tissue obtained from the archives of the Manhattan Brain Bank at Mt. Sinai School of Medicine, which had been previously fixed in 10% buffered formalin and embedded in paraffin, was sectioned at a thickness of 4 μm. After deparaffination and antigen retrieval with citrated buffer heated to 97°C, a primary anti-Tat antibody was applied overnight at room temperature (courtesy of Avindra Nath, Department of Neurology, Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD). After being rinsed thoroughly with PBS, samples were incubated with a Texas red-tagged secondary antibody for 1 h. Then rabbit polyclonal antiagnoprotein antibody (24) was incubated overnight, and finally, after a thorough rinsing with PBS, a fluorescein-tagged secondary antibody was incubated and sections were visualized in an inverted, fluorescent Nikon microscope with deconvolution software (SlideBook 4.0.1.34; Intelligent Imaging, Denver, CO). The JCV late regulatory product, agnoprotein, is detected in the cytoplasm of the same astrocytes (B; fluorescein). Superimposition of both fluorochromes shows colocalization of both proteins in the cytoplasm (arrow) of the majority of cells and in the nuclei (arrowhead) of few bizarre astrocytes (C; double labeling). (D to F) Primary astrocytes were coinfected with HIV-1 and JCV, and by immunofluorescence we detected Tat in both nuclei and cytoplasm of infected cells (D; rhodamine), and agnoprotein in the cytoplasm (E; fluorescein). Deconvolution demonstrates the colocalization of both proteins in the cytoplasmic compartment (F). (G to I) U-87MG cells cotransfected, as previously described (20), with plasmids expressing Tat (CFP-Tat) and agnoprotein (YFP-agnoprotein) show Tat localization mainly in the nuclei, with some cells showing nuclear and cytoplasmic labeling (G), and agnoprotein in the cytoplasm (H), where it colocalizes with Tat (I). Original magnification in all panels, ×1,000. YFP-agnoprotein has been previously described (20). CFP-Tat was created by removing the Tat gene from cytomegalovirus (CMV)-Tat with BglII and EcoRI and cloning it into the BamHI and EcoRI sites of pECFP-C1.