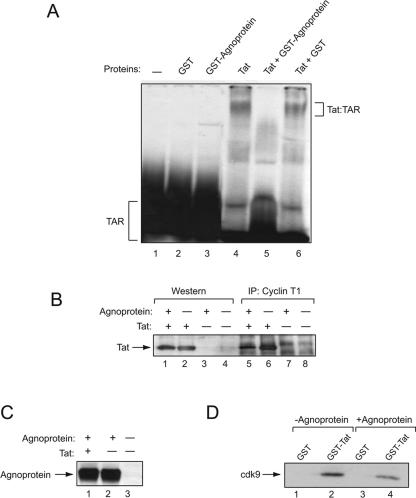
FIG. 6.
Effect of agnoprotein on the interaction of Tat with TAR and cyclin T1. (A) Electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Approximately 60,000 cpm of synthetic 32P-labeled TAR RNA (5′UGGGUCUCUCUGGUUAGACCAGAUCUGAGCCUGGGAGCUCUCUGGCUAACUAGGGAACCCACUGCUUAAGCCUCA-3′) was incubated for 1 h on ice with 0.3 μM eluted GST, GST-agnoprotein, or in vitro-synthesized Tat in 20 μl binding buffer containing 12 mM HEPES (pH 7.9), 4 mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.5), 60 mM KCl, 5 mM MgCl2, 0.8 mM dithiothreitol, 0.5 μg of poly(dI-dC) as nonspecific competitor, 10% glycerol, and 10 μg/ml DNase-free RNase. The binding mixture was resolved on a 6% polyacrylamide-0.5× TBE gel and analyzed by autoradiography. Integrity and equal loading of proteins used in the assay were verified by SDS-PAGE. (B) Agnoprotein negatively affects binding of Tat to cyclin T1. HL3T1 cells (HeLa cells with stably integrated HIV-1 LTR in the genome) were transfected with plasmids expressing Tat or agnoprotein alone or in combination. Total protein extract was prepared, and 250 μg was incubated with an anti-cyclin T1 antibody. Immunocomplexes were immunoprecipitated (IP) with the addition of protein A-Sepharose beads, resolved by SDS-PAGE, and analyzed by Western blotting using an anti-Tat antibody. The presence of Tat was verified by Western blotting (lanes 1 to 4). Radiograms were analyzed by the Quantity One program (Molecular Imager FX; Bio-Rad), and binding activity was determined by analyzing the intensity of bands (adjusted volume of counts per mm2). A total of 12.5% of Tat was bound to cyclin T1 in the absence of agnoprotein, and only 3% of Tat was found in the complex with cyclin T1 in the presence of agnoprotein. (C) Expression of agnoprotein in the transfected cells was tested by Western blot analysis. (D) Presence of agnoprotein affects binding of Tat to cdk9. Total protein extracts from U-87MG cells transfected with pCDNA3 or pCMV-agnoprotein were incubated with either GST or GST-Tat 1-86 immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads. After washing, protein complexes were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by Western blotting using anti-cdk9 antibody. GST proteins were used at a 1 μM concentration in pull-down assays.