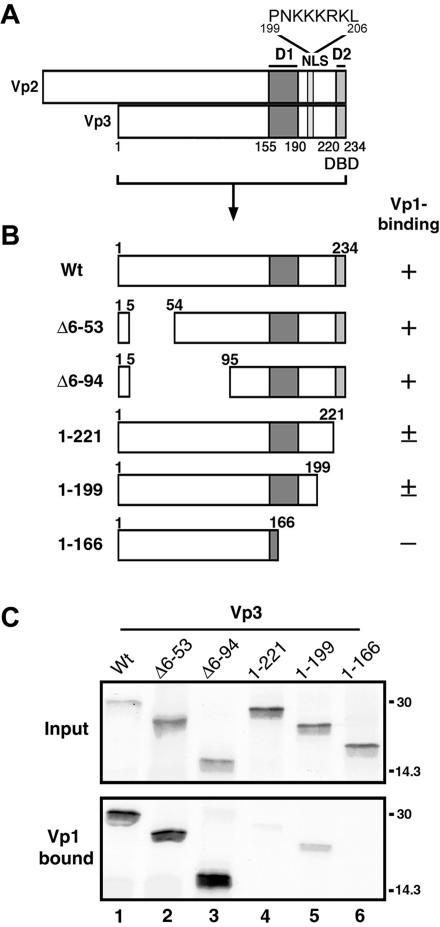
FIG. 1.
In vitro interaction of truncated Vp3s and the Vp1 pentamer. (A) Functional Vp3 sequence elements. Minor capsid proteins Vp2 and Vp3 share identical amino acids, except for a Vp2-unique segment of 118 residues; hence, the shared regions are denoted by Vp3 amino acids as follows: D1, Vp3 residues 155 to 190; D2, Vp3 residues 222 to 234; and NLS, Vp3 residues 199 to 206 (whose sequence is shown). (B) Schematic diagram of truncated Vp3s used in the Vp1 pentamer binding assay. The first and last Vp3 residue numbers in the fragments are shown in each diagram. The abilities of the Vp3 fragments to bind to Vp1ΔC58 as shown in Fig. 1C are categorized by +, ±, and −, describing strong, weak, and undetectable, respectively. (C) Vp1ΔC58 pentamer was incubated with 35S-methionine labeled wild-type or truncated Vp3s and retrieved by metal-chelate beads. The Vp3s bound to the beads were visualized by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. The upper panel (Input) and lower panel (Vp1 bound) show 1/25 of the total 35S-labeled Vp3 used and 1/3 of the total 35S-labeled Vp3 bound to the beads, respectively. Positions for the molecular-mass marker, 30 and 14.3 kDa, are marked on the right side of the panels. Vp3 ORFs used for binding assays are as follows: lane 1, full-length Vp3 (Wt); lane 2, Δ6-53; lane 3, Δ6-94; lane 4, residues 1 to 221; lane 5, residues 1 to 199; and lane 6, residues 1 to 166.