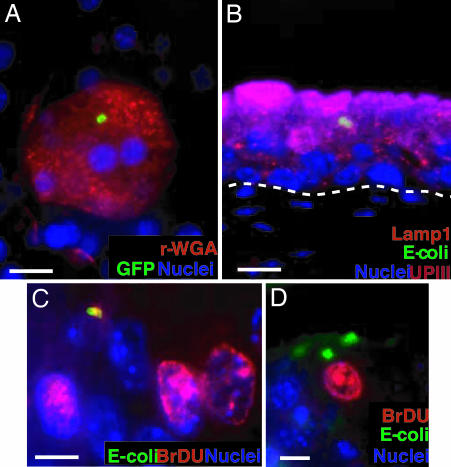
Fig. 1.
QIRs form within Lamp1+ vesicles in superficial facet cells. (A) Epifluorescence microscopy on whole-mounted bladders infected with GFP+UTI89 showing bacterial QIRs (green) persisting in differentiated facet cells stained with Alexa Fluor 94-tagged wheat germ agglutinin (r-WGA, to demarcate outlines of facet cell membranes). Epithelial nuclei stained with bis-benzimide appear blue. (Scale bar, 50 μm.) (B) Lamp1+ vesicles (orange, stained with Alexa Fluor 594-tagged rat antibody to Lamp1) containing QIRs (green, stained with Alexa Fluor 88-tagged rabbit polyclonal Abs to E. coli) are in UPIII+ terminally differentiated facet cells (purple with Alexa Fluor 47-tagged mouse mAb to UPIII) 2 weeks after infection. (Scale bar, 50 μm.) The dashed line demarcates epithelial–mesenchymal boundary. (C and D) IFA of tissue sections from BrdU-injected bladders of infected mice show a small BrdU+ (red; stained with Alexa Fluor 94-tagged goat polyclonal antibodies to BrdU) bacterial QIR (yellow) and BrdU+ transitional epithelial cells. A larger BrdU− QIR (green) is depicted in D. (Scale bar, 10 μm.)