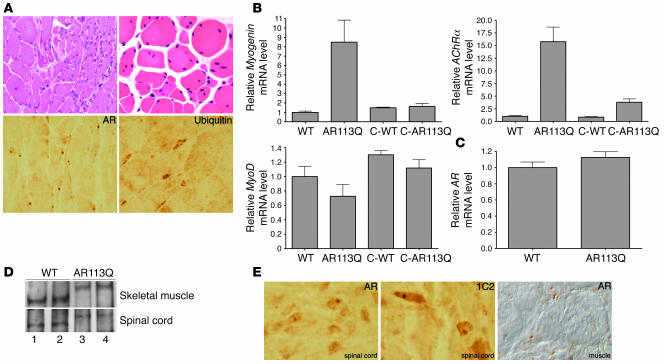
Figure 2. Neuromuscular pathology in AR113Q male mice.
(A) Grouped atrophic, angulated fibers (upper left) and marked variation in fiber size and internally placed nuclei (upper right) are present in hind-limb skeletal muscle of AR113Q males. Magnification, ×400 (upper left); ×1000 (upper right). AR (lower left) and ubiquitin (lower right) immunoreactive intranuclear inclusions are also present. Magnification, ×1000. (B) Relative myogenin, acetylcholine receptor α-subunit (AChRα), and MyoD mRNA expression levels in hind-limb muscle as determined by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Data are from WT (n = 8), AR113 (n = 8), and castrated WT males (C-WT) (n = 6) at 3–5 months and castrated AR113Q males at 18 months (n = 4). Results are reported as mean ± SD relative to expression of 18s rRNA. Expression levels of myogenin and acetylcholine receptor α-subunit mRNA in AR113Q muscle are significantly different from those in all other groups (P < 0.01 and P < 0.001, respectively, by ANOVA with the Neuman-Keuls multiple comparison test). Expression of MyoD mRNA in AR113Q and WT muscle is not significantly different. (C) Relative AR mRNA expression levels in hind-limb muscle of WT (n = 8) and AR113Q males (n = 8) at 3–5 months (P > 0.05). (D) AR protein expression in skeletal muscle (top panel) and spinal cord (bottom panel) of WT (lanes 1 and 2) and AR113Q males (lanes 3 and 4) at 3–4 months detected by immunoprecipitation and Western blot. (E) Intranuclear inclusions in spinal cord and skeletal muscle of AR113Q mice at 24 months detected by immunohistochemistry for AR and expanded glutamine tract (1C2). Magnification, ×1000.