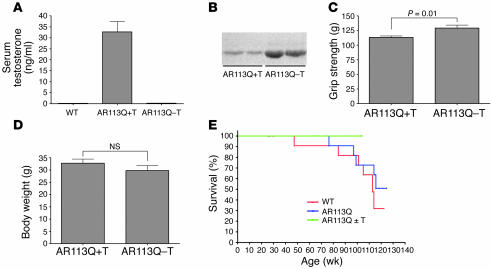
Figure 4. Testosterone-treated AR113Q females exhibit normal life span.
(A–D) Testosterone-dependent effects on heterozygous AR113Q females. AR113Q females were implanted with testosterone (+T, n = 8) or vehicle control (–T, n = 7) pellets at 2–4 months. Serum testosterone levels, determined at 4–7 months, were significantly increased in hormone-treated mice compared with controls (P < 0.001) (A). Excretion of major urinary proteins (B) was compared in AR113Q–T and AR113Q+T females. AR113Q+T females showed a small but significant deficit in forelimb grip strength (C) (P = 0.01 by unpaired Student’s t test) but unchanged body mass (D) (P = 0.3 by unpaired Student’s t test) compared with AR113Q–T females at 16 months. (E) Survival curves of AR113Q+T (n = 8) and AR113Q–T (n = 7) (overlapping green lines), untreated AR113Q females (blue line, n = 11), and WT females (red line, n = 19) were similar (P > 0.05). None of the AR113Q+T or AR113Q–T females died during the study; half were euthanized at 16–19 months, and the remainder were euthanized at 23–26 months.