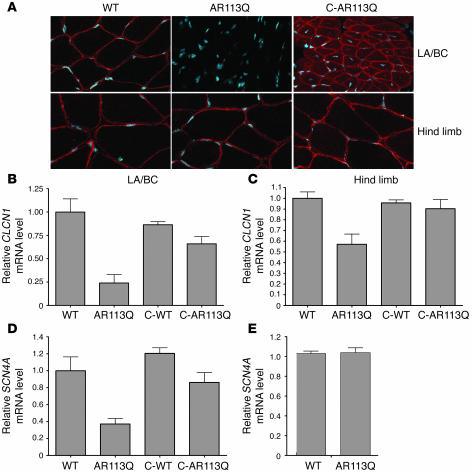
Figure 6. Androgen-dependent decrease of CLCN1 and SCN4A expression in AR113Q skeletal muscle.
(A) Indirect immunofluorescence demonstrates CLCN1 protein expression (red) in levator ani/bulbocavernosus (LA/BC) and hind-limb muscles of WT, AR113Q, and castrated AR113Q males. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. (B–D) Relative CLCN1 (B and C) and SCN4A (D and E) mRNA expression levels in levator ani/bulbocavernosus (B and D) and hind-limb (C and E) muscles of WT (n = 8), AR113Q (n = 9), and castrated WT males (n = 6) at 3–5 months and castrated AR113Q males at 18 months (n = 4). Data are reported as mean ± SD relative to expression of 18s rRNA. Differences between WT and AR113Q are significant different in hind-limb (P < 0.01 for CLCN1) and levator ani/bulbocavernosus muscles (P < 0.001 for CLCN1 and SCN4A) as determined by ANOVA with the Neuman-Keuls multiple comparison test. SCN4A levels in hind-limb muscle are not significantly different.