Figure 1.
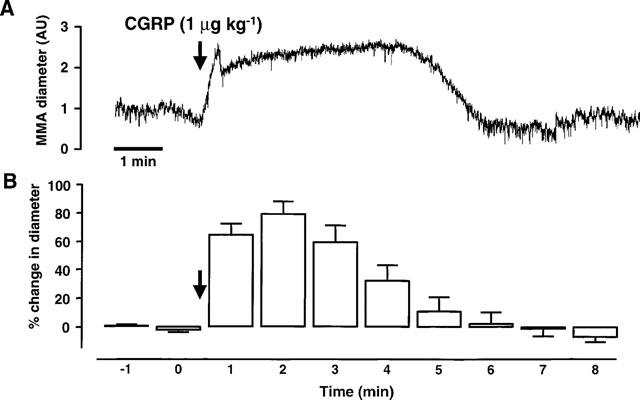
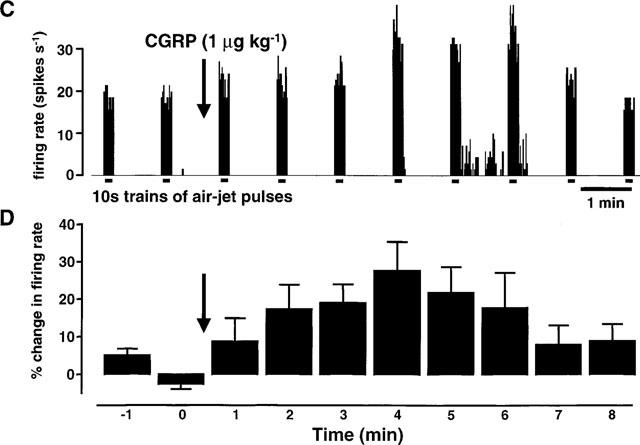
This figure shows the effects of rat-αCGRP (1 μg kg−1; i.v.) on the middle meningeal artery (MMA) diameter and on neuronal activity from the trigeminal dorsal horn. The top trace (A) shows an original experimental record of the MMA diameter in arbitrary units (AU). The mean responses from 12 CGRP applications in ten rats (B) are displayed as the percentage change in MMA diameter relative to the pre-CGRP control period. The effects of CGRP-evoked vasodilation on trigeminal neuronal activity are shown in the third trace (C). In this panel extracellular, single unit action potentials are displayed as the firing rate (spikes s−1) response to innocuous stimulation of the vibrissae using an air-jet. The mean data (D) from 12 cells are shown as the percentage change in neuronal activity relative to the mean of three pre-CGRP stable controls. (A) and (C) are time-matched data from the same experiment and (B) and (D) are mean data from simultaneous recordings of MMA diameter and neuronal activity following application of CGRP.
