Figure 1.
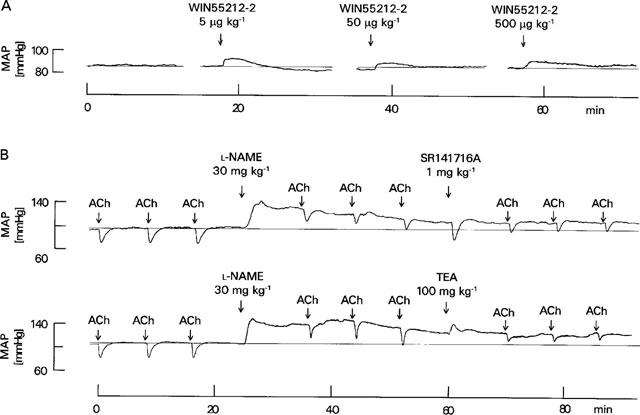
(A) Effect of WIN55212-2 on mean arterial pressure (MAP) in a pithed rabbit in which blood pressure was raised by an infusion of noradrenaline (2 μg kg−1 min−1)–original tracing representing four experiments with similar results (the average values are shown in Niederhoffer & Szabo, 1999). WIN55212-2 was injected as indicated by arrows; the slight increase in blood pressure after injection of WIN55212-2 is due to the solvent. (B) Effects of L-NAME, SR141716A and TEA on the acetylcholine (ACh, 1 μg kg−1)-evoked decrease in mean arterial pressure (MAP) in pithed rabbits–original tracings. Blood pressure was raised by an infusion of noradrenaline (2 μg kg−1 min−1) and indomethacin (5 mg kg−1) was administered 10 min before the first acetylcholine injection. Other drugs were injected as indicated by arrows.
