Figure 5.
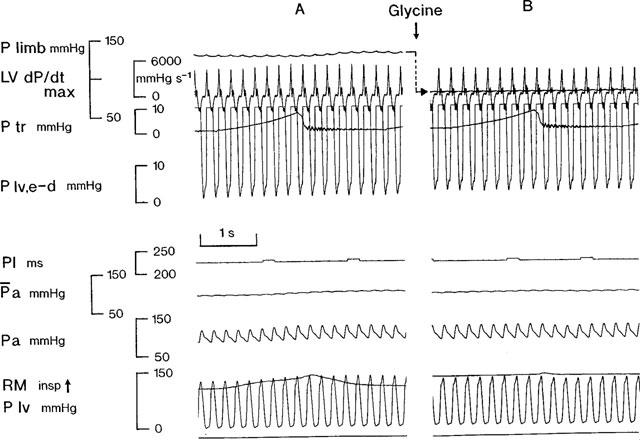
Artificially ventilated anaesthetized cat: traces showing the effects of topical application to the ‘glycine-sensitive area' of the ventrolateral medulla of glycine, 500 μg each side, after previous application of DOI and NMDA. The heart was electrically paced and the mean arterial blood pressure was maintained constant. Control panel A was taken 1 min before the application of glycine, panel B 3 min into the test. Records from above downwards: P limb, hindlimb mean perfusion pressure; LV (left ventricular) dP/dt max; Ptr, tracheal pressure; P lv, e-d, left ventricular end-diastolic pressure; PI, pulse interval; Pa, 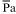 , phasic and mean arterial blood pressure; RM, respiratory movements; P lv, left ventricular pressure. Time calibration, 1 s. For clarity, the change in position of the P limb trace between panels A and B is shown by the arrow.
, phasic and mean arterial blood pressure; RM, respiratory movements; P lv, left ventricular pressure. Time calibration, 1 s. For clarity, the change in position of the P limb trace between panels A and B is shown by the arrow.
