Figure 4.
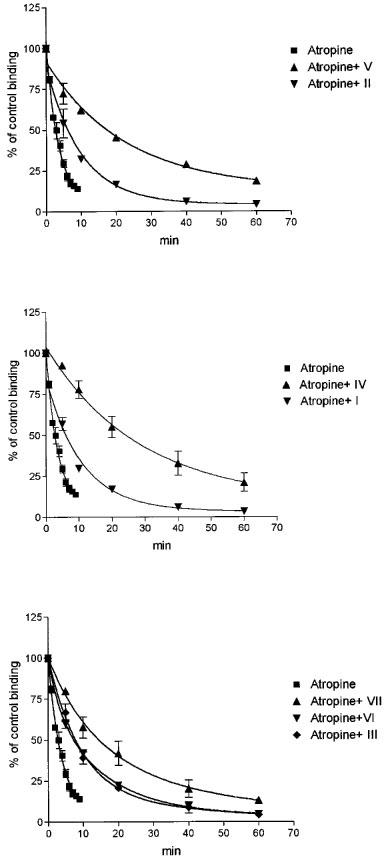
Effects of α-truxillic acid esters applied at a single concentration of 10 μM on the rates of atropine-induced dissociation of [3H]-NMS from muscarinic receptors of the M2 subtype. Membranes were preincubated in medium A for 60 min with 250 pM [3H]-NMS, after which 5 μM atropine was added either alone or simultaneously with 10 μM ester. Abscissa: Time (min) after the addition of atropine. Ordinate: [3H]-NMS binding, expressed as per cent of the binding immediately before the addition of atropine. Top panel: effects of the bis-3-piperidylpropyl ester (compound II) and of its N-ethyl derivative (compound V). Middle panel: effects of the bis-diethylaminopropyl ester (compound I) and its bis-N-methyl derivative (compound IV). Bottom panel: effects of the bis-4-piperidylbutyl ester (compound III), its bis-N-methyl derivative (compound VI) and bis-N-ethyl derivative (compound VII). Data are means±s.e.mean of two experiments with incubations performed in duplicates. The koff value computed for the rate of dissociation observed after the addition of atropine was 0.239 min−1 and the dissociation was decelerated 2.8, 2.2, 8.9, 2.2, 5.4, 2.8 and 2.8 fold when compounds V, II, IV, I, VII, VI and III, respectively, were added together with atropine.
