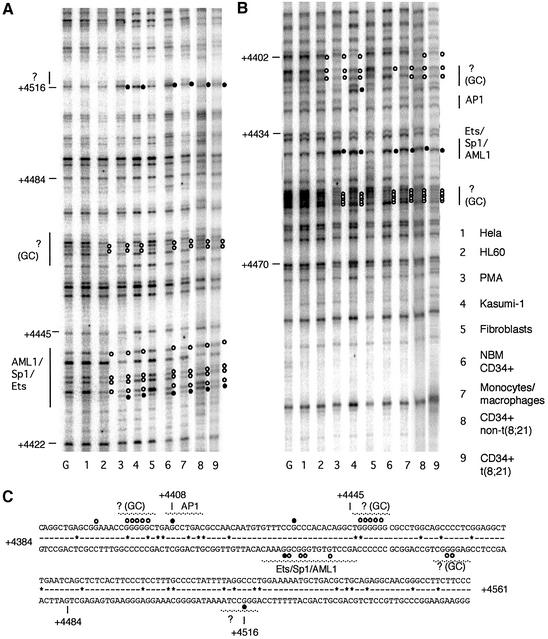
Fig. 4. In vivo DMS footprinting of the human c-FMS intronic regulatory element (FIRE) reveals extensive protections and enhancements of DMS reactivity on both DNA strands. (A) The lower DNA strand shows extensive protections particularly over the AML1/SP-1/Ets-binding site which are present with varying penetration in all c-FMS-expressing cells. There are further protections in these cells over a GC-rich region at +4450. (B) The upper DNA strand has protections of GC-rich regions flanking the AML1/Sp1/Ets site, which has a prominent enhancement of G +4434 in normal bone marrow CD34+ cells, CD34+ blast cells from leukaemia patients (P2 and P9), Kasumi-1, PMA-treated HL60 and primary macrophages. (C) The FIRE sequence, with protections and enhancements indicated as white and black filled circles, respectively. Sequences conserved between mouse and man are indicated by a line; sequence deviations are displayed as (*). G, G reaction with naked DNA.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.