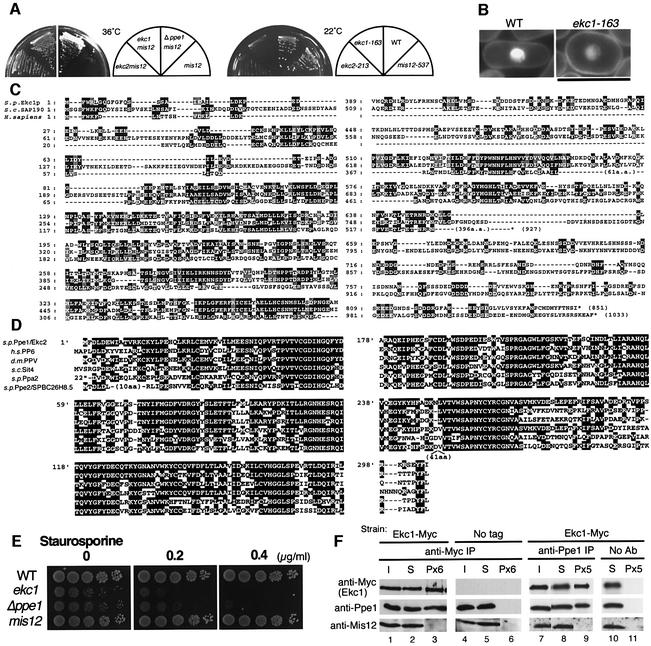
Fig. 1. Extragenic suppression of mis12-537 by ppe1 and ekc1 mutants. (A) Left: double mutants mis12-537 ekc1-163, mis12-537 ekc2-213 and mis12-537 Δppe1 could form colonies at 36°C, whereas single mis12-537 did not. Right: single ekc1 and ekc2 mutants were cold sensitive and unable to form colonies at 22°C. (B) ekc1-163 is pear-shaped even at the permissive temperature. Bar, 10 µm. (C) Amino acid sequence alignment of S.pombe Ekc1, S.cerevisiae SAP190 and Homo sapiens KIAA0685. Identical residues are boxed, and similar residues are hatched. Saccharomyces cerevisiae has four SAPs (SAP4, 190, 185 and 155), while human has three similar sequences (KIAA0685, KIAA1115 and KIAA1558). (D) Sequence alignment of S.pombe Ppe1 phosphatase, S.cerevisiae Sit4, H.sapiens PP6, D.melanogaster PPV and S.pombe Ppa2 and Ppe2/SPBC26H8.05. (E) Exponentially growing wild-type, ekc1, ppe1 and mis12 cells were spotted after dilution onto YPD plate that contained 0.2 or 0.4 µg/ml staurosporine, and incubated at 33°C. (F) The strain containing the integrated Ekc1-Myc was immunoprecipitated by anti-Myc antibodies (lanes 1–3) and anti-Ppe1 antibodies (lanes 7–9), and immunoblotting was used to detect the three proteins Ekc1, Ppe1 and Mis12 in the resulting precipitates. Beads without antibodies (lanes 10 and 11) or the strain without myc epitopes (lanes 4–6) were used as control. I, input; S, supernatant; P, immunoprecipitate. Equal amounts of I and S were loaded, whereas immunoprecipitates were 6- (Px6) or 5-fold (Px5) concentrated.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.