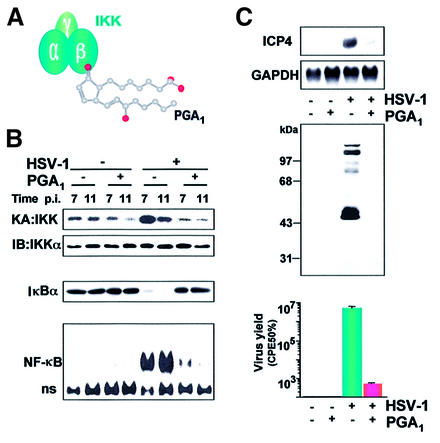
Fig. 4. Effect of inhibition of IKK activity on HSV-1 replication. (A) Structure of PGA1. PGA1 and other cyclopentenone prostanoids possess a reactive α,β-unsaturated carbonyl group in the cyclopentane ring which is responsible for binding and inactivating the β-subunit of the IKK complex, resulting in the block of NF-κB activation. (B) PGA1 treatment (30 µM) inhibits HSV-1-induced IKK and NF-κB activity, and prevents IκBα degradation in HEp-2 cells. At 7 and 11 h after infection (p.i.), whole-cell extracts were analyzed for endogenous IKK activity and recovery by kinase assay (KA) and immunoblotting (IB), respectively (top panels), for IκBα degradation by immunoblot analysis (middle panel), and for NF-κB activation by gel shift analysis (bottom panel). (C) In HSV-1-infected HEp-2 cells, PGA1 treatment causes a reduction in the levels of viral mRNA (ICP4, determined by northern blot analysis at 8 h p.i., upper panel), and of viral proteins (determined by western blot analysis, medium panel) and virus yield (determined by CPE50% assay, bottom panel) at 24 h p.i. (Amici et al., 2001).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.