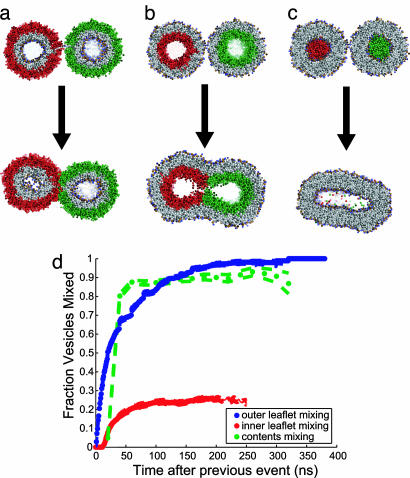
Fig. 4.
Measuring the progress of fusion via analogue to experiment. Progress of the vesicle fusion reaction is assessed via lipid and vesicle contents mixing, as have been measured in experimental assays (23, 28, 29). (a) Mixing of outer leaflet lipids. (b) Mixing of inner leaflet lipids. (c) Mixing of vesicle contents. (d) The fraction of vesicles that have mixed inner leaflet lipids, outer leaflet lipids, and contents, measured for each mixing event as a function of Δt from the time of the previous mixing event. Outer leaflet mixing is rapid and complete, but on the time scale of individual trajectories, only 26% of inner leaflets fuse; the remaining vesicles fuse at a much slower rate, dependent on the decay of off-pathway intermediates. Upon inner leaflet fusion, formation of a fusion pore and contents mixing is again rapid and complete. Dashed lines represent one standard deviation of the mean. Intravasicle lipid mixing between leaflets was observed in <2% of trajectory snapshops (Fig. 13, which is published as supporting information on the PNAS web site).