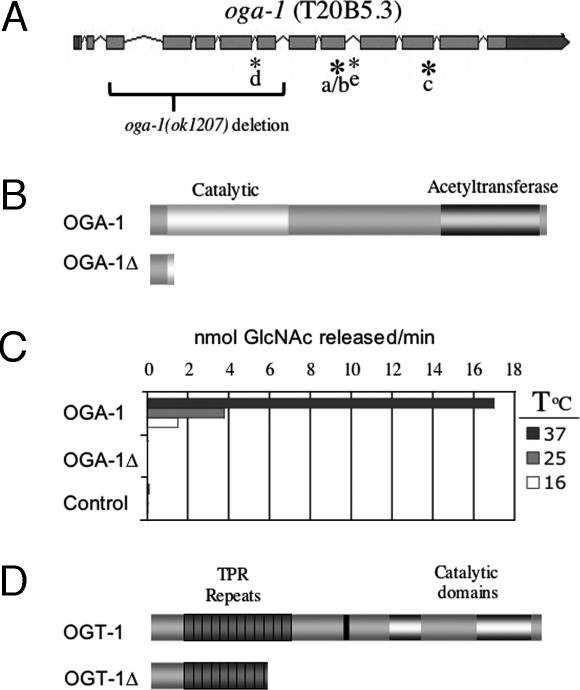
Fig. 1.
The C. elegans oga-1 gene. (A) A schematic of the oga-1 gene showing coding regions shaded light gray and noncoding regions shaded dark gray. We have confirmed four different splice variants (b–e). Novel sequences have been assigned the GenBank accession numbers: DQ407521, DQ407522, and DQ407523. Large bold asterisks indicate use of alternative 3′ splice sites, and small asterisks indicate in-frame utilization of the entire intron. The nine clones we isolated all have an insertion of 17 codons at the 3′ end of exon 9 in the coding sequence of presumptive isoform a. This insertion of 17 codons forms our canonic transcript, oga-1b (5/9 clones). Transcript oga-1c has two additional codons from exon 11 (2/9 clones). Two novel transcripts, d (1/9 clones) and e (1/9 clones), differ from the canonic oga-1b by inclusion of intron 5 or 9 sequences, respectively. Brackets indicate the oga-1(ok1207) deletion joining exon 3 with intron 7, producing a 41-aa protein with 13 novel amino acids. (B) The domain structure of OGA-1 reveals an OGA glycosidase catalytic domain and a region with homology to acetyltransferases. The truncated protein produced by the oga-1(ok1207) deletion allele, OGA-1Δ, lacks both catalytic domains. (C) Enzyme activity of recombinant C. elegans proteins was measured by using the OGA activity assay and normalized to equal amounts of epitope-tagged OGA-1 protein as described in Materials and Methods. The negative control is the PET43.1 expression vector, with human mOGT as insert. A positive control (data not shown in the graph) human OGA was found to release 120, 70, and 27 pmol of GlcNAc per min at 37°C, 25°C, and 16°C, respectively. (D) The ogt-1(ok430) deletion allele generates a truncated protein of 465 aa (OGT-1Δ) that lacks catalytic activity, as described (26).