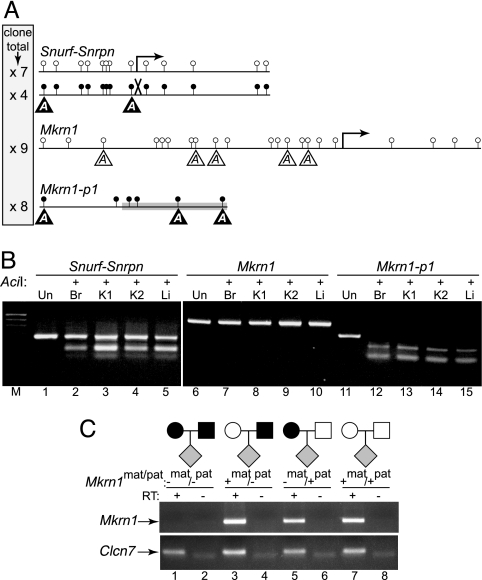
Fig. 3.
Epigenetic analyses. (A) Sequence analysis of bisulfite converted loci. The methylation status of Mkrn1-p1, Mkrn1, and the imprinted Snurf-Snrpn loci in WT kidney DNA were determined by bisulfite sequencing of individual clones. Amplicons of each locus are shown with lollipops representing unmethylated (open circle) or methylated (closed circle) cytosines in CpG dinucleotides, with the number of clones of a given type for each locus shown in the shaded box at left. Arrows, transcriptional start sites (Mkrn1 and paternally expressed Snurf-Snrpn); X, silenced maternal Snurf-Snrpn allele; gray box, 5′ end of Mkrn1-p1; reverse-shaded As in triangles, AciI digestion sites diagnostic for the methylated allele (unshaded As for Mkrn1 represent a hypothetical methylated allele). (B) Biallelic methylation status. AciI will digest only bisulfite-converted amplified DNA that was originally methylated (see A for potential sites). Br, brain DNA; K1, same kidney DNA as in A; K2, kidney DNA from another WT mouse; Li, liver DNA; Un, undigested PCR products pooled from each tissue (lanes 1, 6, 11); M, 100-bp ladder. (C) Mkrn1 is not imprinted. RT-PCR was performed on RNA (RT−) and cDNA (RT+) samples from Mkrn1 gene-trapped (mat pat, −/−), heterozygous (mat pat, +/−; mat pat, −/+), or WT (mat pat, +/+) mice by using exon 4 and 5 primers (Upper) or Clcn7 control primers (Lower). RNA obtained from mice (gray diamonds) derived from the illustrated matings was used for RT-PCR (black symbols, gene-trapped Mkrn1 allele; white symbols, WT Mkrn1 allele).