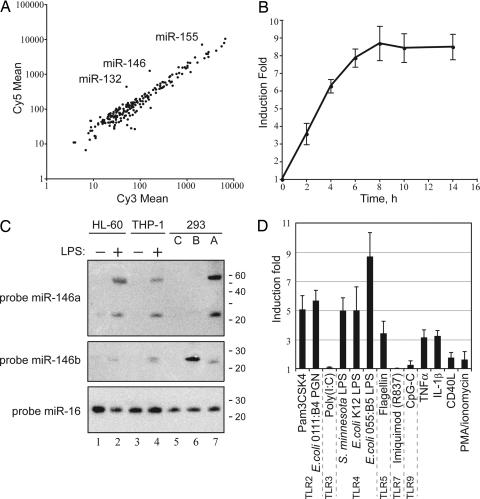
Fig. 1.
miRNA miR-146a is an immediate early-response gene induced by various microbial components and proinflammatory mediators. (A) Microarray analysis of miRNA expression in THP-1 cells after stimulation with LPS (E. coli strain 055:B5). The scatter plot shows averaged (n = 4) background-subtracted raw intensities for each probe on both channels for Cy3-labeled control and Cy5-labeled 8-h LPS-treated samples. Each dot represents one miRNA probe. (B) Kinetics of miR-146a up-regulation by LPS. THP-1 cells were stimulated with LPS for the indicated times, and miR-146 expression was analyzed by qPCR and normalized by using 5S RNA levels. (C) Northern blot analysis of miR-146a/b expression. Indicated human cell lines were treated with LPS (E. coli strain 055:B5) for 8 h and probed with DNA oligonucleotides complementary to mature miR-146a (Top) and miR-146b (Middle). To assess the specificity of the probes, we used total RNA from 293 cells transiently transfected with pcDNA3 vector or expression plasmids for either pre-miR-146a or pre-miR-146b (marked as C, A, and B, respectively). (The faint bands in the lanes probed for miR-146b are cross-reactions with mirR-146a bands; the dark band in lane 6 represents miR-146b.) The membrane was reprobed for miR-16 as a loading control (Bottom). Radiolabeled RNA decade marker was used as a molecular weight reference. (D) Analysis of miR-146 expression in response to a panel of innate immunity ligands. THP-1 cells were stimulated with the indicated stimuli for 8 h. miR-146 expression was analyzed by qPCR and normalized by using 5S RNA levels.