Fig. 2.
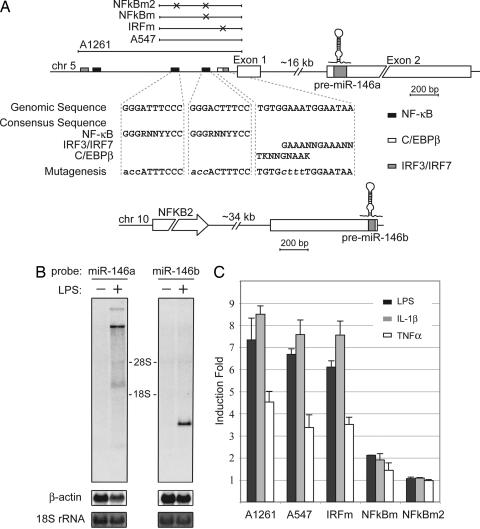
miR-146a is an NF-κB-dependent gene. (A) Schematic diagrams of miR-146a (Upper) and miR-146b (Lower) genomic loci on human chromosomes 5 and 10, respectively. Putative binding sites of NF-κB (black), IRF3/7 (gray), and C/EBPβ (white, partially overlaps with IRF3/7) transcriptional factors are shown as boxes. Genomic regions indicated by bars above the miR-146a locus were analyzed in promoter luciferase reporter assay (C). Mutations, disrupting transcription factor binding introduced in the A547 construct, are indicated by X, and the sequences of mutated sites are shown under the locus diagram. (B) Northern blot analysis of pri-miR-146a and pri-miR-146b expression in the THP-1 cell line. Cells were starved for 24 h and then stimulated with LPS for 8 h. Northern blots were hybridized with radiolabeled pre-miR-146a or pre-miR-146b probes, respectively. β-Actin (Northern blot) and 18S rRNA (methylene blue staining) levels are shown as loading controls. (C) miR-146a promoter analysis. Promoter constructs containing genomic fragments of miR-146a locus were transfected into the 293/IL-1R/TLR4/MD2 cell line. Cells were stimulated with TNFα (white bars), IL-1β (gray bars), or LPS (black bars) for 8 h and analyzed by luciferase reporter assay. Promoter regions used in this experiment are depicted schematically in A.