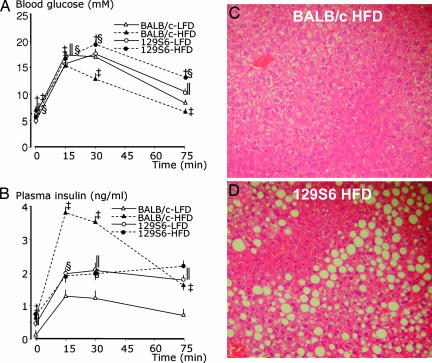
Fig. 1.
Pathophysiology of the response of BALB/c and 129S6 mice to prolonged fat-feeding. Effect of glucose injection on blood glucose (A) and plasma insulin (B) concentrations in BALB/c and 129S6 mice fed an LFD or HFD. H&E-stained liver sections from 5-month-old BALB/c (C) and 129S6 (D) mice on HFD, showing micro- and macrovesicular steatosis in 129S6 mice (magnification, ×20). Plasma glucose and insulin values were obtained from >53 (BALB/c-LFD), 34 (BALB/c-HFD), and 40 (129S6-LFD, 129S6-HFD) mice. Significant differences (P < 0.05) between HFD-fed and LFD-fed 129S6 mice (†), between HFD-fed and LFD-fed BALB/c mice (‡), between LFD-fed 129S6 and BALB/c mice (‖), and between HFD-fed 129S6 and BALB/c mice (§) are shown.