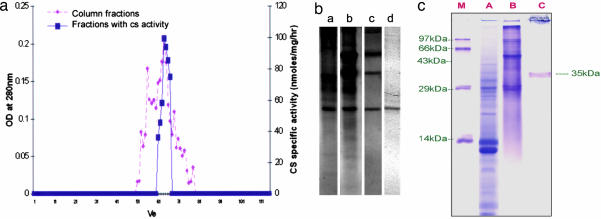
Fig. 2.
Purification of CS. (a) Elution and specific activity profile of CS through Sephadex G-100. The ammonium sulfate fraction (60%) was loaded in to a gel filtration chromatography column (G-100) that was equilibrated with 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer at 12 ml/h. Of 110 fractions collected, CS activity was performed for every alternate fraction, and active fractions were bulked and lyophilized. Subsequently lyophilized active CS fractions were loaded to amino H Sepharose column bound with vanillylamine (5 mg/ml). The unbound fractions were collected in 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer, and the bound fractions were eluted in 1 M NaOH and subjected to CS assay after dialysis against 0.1 M potassium phosphate buffer. (b) Native gel (10%) depicting purified CS. Lanes: a, crude placental protein extract; b, 60% ammonium sulfate fractionated placental protein; c, Sephadex G-100 column eluted fractions; d, AH-Sepharose column eluted fraction. (c) SDS/PAGE (12.5%) showing purified CS. Lanes: M, protein molecular weight marker; A, ammonium sulphate fractionated placental protein; B, Sephadix G-100 column eluted fractions; C, AH-Sepharose column eluted fraction.