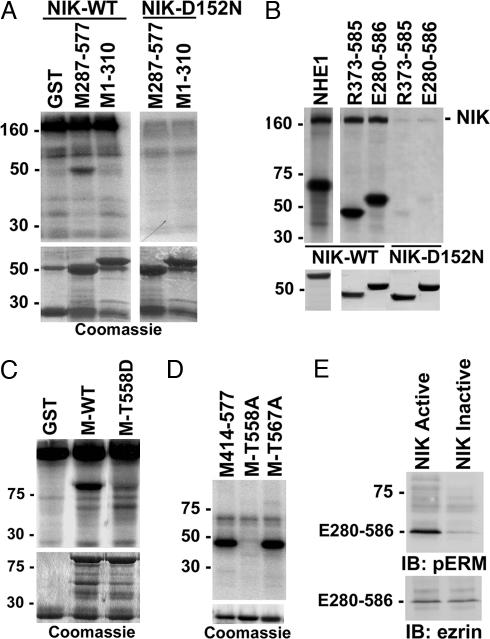
Fig. 2.
NIK directly phosphorylates the C terminus of ERM proteins. (A) Autoradiograms of kinase reaction (Upper) and Coomassie-stained fusion proteins (Lower) are shown. Myc-tagged WT NIK or NIK-D152N was expressed in COS-7 cells, immunoprecipitated, and used for in vitro kinase assays with GST or GST-fusion proteins containing moesin C terminus (M287-577) or N terminus (M1-310). The high-molecular-mass band at 160 kDa corresponds to autophosphorylated NIK. (B) Autoradiograms of kinase reaction (Upper) and Coomassie-stained fusion proteins (Lower) are shown. WT NIK or NIK-D152N was expressed, immunoprecipitated, and reacted in vitro with GST fusion proteins containing the C terminus of NHE1, radixin (R373-585), or ezrin (E280-586). (C) Autoradiograms of kinase reaction with WT NIK as in A and B (Upper) and Coomassie-stained fusion proteins (Lower) are shown. GST and fusion proteins containing full-length moesin WT (M-WT) or moesin with T558 substituted with aspartic acid (M-T558D) were used as substrates. (D Upper) Autoradiogram of kinase reaction with purified NIK domain (amino acids 22–374) and fusion proteins of the C terminus of moesin WT (M414–577) or containing single substitutions of Thr-558 or Thr-567 with alanine (M-T558A and M-T567A, respectively) is shown. (D Lower) Coomassie-stained fusion proteins used for kinase reaction are shown. (E) Immunoblots (IB) with antiphospho-ERM antibodies (Upper) and antiezrin antibodies (Lower) of C-terminal ezrin translated in vitro and incubated with purified NIK domain active or inactivated by boiling are shown.