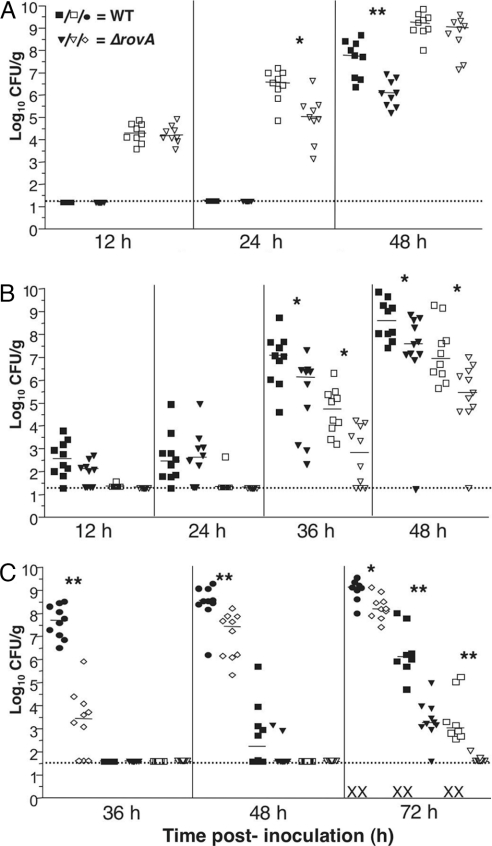
Fig. 1.
Virulence analysis of the ΔrovA mutant by different routes of infection. (A–C) Dissemination analysis of CO92 and the ΔrovA mutant. Ten mice per strain for each time point analyzed were infected s.c. (102 cfu) (C), i.n. (104 cfu) (A), or i.p. (102 cfu) (B) with CO92 or ΔrovA. Infection was allowed to progress for the indicated time, and mice were then killed to harvest superficial cervical lymph nodes (filled circle, wild type; open diamonds, ΔrovA mutant), spleens (filled squares, wild type; filled triangles, ΔrovA mutant), and lungs (open squares, wild type; open triangles, ΔrovA mutant). Colonization of bacteria was quantified by enumerating viable cfu in each organ. Each symbol represents a single mouse, and these results are the composite of two independent experiments. The limit of detection is indicated by the dotted line, and symbols in the dotted line indicate cfu below the limit of detection. The X symbol on the x axis denotes dead mice at the designated time point. Significance was assayed by using Student’s t test with a two-tailed nonparametric analysis. For statistically significant comparisons, single asterisks indicate P ≤ 0.05, and double asterisks indicate P ≤ 0.005.