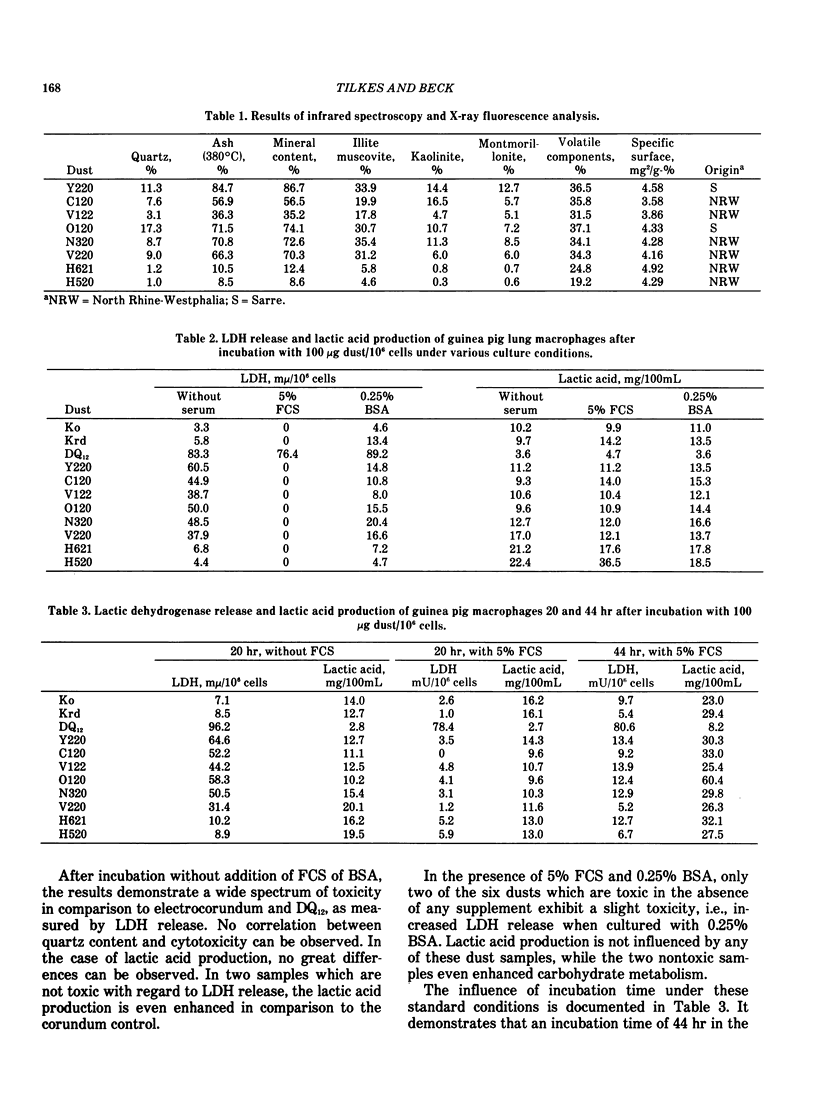
Abstract
The effects of the standard dusts, electrocorundum, and Dorentruper quartz (DQ12), as well as mine dusts have been tested in guinea pig lung macrophage cultures. The parameters compared were: release of lactic dehydrogenase for demonstration of plasma membrane permeability and production of lactic acid as an indicator of carbohydrate metabolism. In addition to the dose-dependent toxicity of different mine, coal and other mineral dusts, we studied the influence of cell culture media and the supplement of fetal calf serum (FCS) and bovine serum albumin (BSA) upon the cell toxicity in this test system. We demonstrated a protective effect of FCS and BSA on dusts of low and medium toxicity, while dusts of high toxicity, like DQ12, were not influenced in their toxicity.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Tilkes F., Beck E. G. Comparison of length-dependent cytotoxicity of inhalable asbestos and man-made mineral fibres. IARC Sci Publ. 1980;(30):475–483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilkes F., Beck E. G. Macrophage functions after exposure to mineral fibers. Environ Health Perspect. 1983 Sep;51:67–72. doi: 10.1289/ehp.835167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


