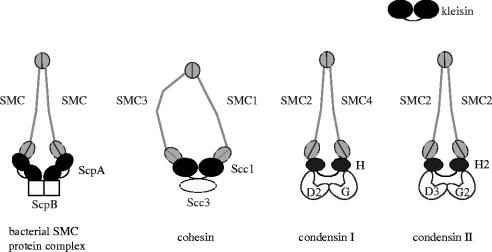
Figure 2.
SMC protein complexes in eukaryotes and bacteria. The B. subtilis SMC protein complex is composed of an SMC homodimer and two regulatory subunits (ScpA and ScpB). The eukaryotic cohesin complex contains a heterodimeric pair of SMC1 and SMC3 and two non-SMC subunits (Scc1 and Scc3). Vertebrate cells possess two different condensin complexes, known as condensin I and condensin II. The two condensin complexes share the same SMC core subunits (SMC2 and SMC4) but differ by their unique sets of non-SMC subunits (CAP-D2, -G, -H for condensin I; CAP-D3, -G2, -H2 for condensin II). Among the non-SMC subunits of these protein complexes, ScpA, Scc1, CAP-H and CAP-H2 are distantly related with each other, belonging to the kleisin superfamily of proteins.