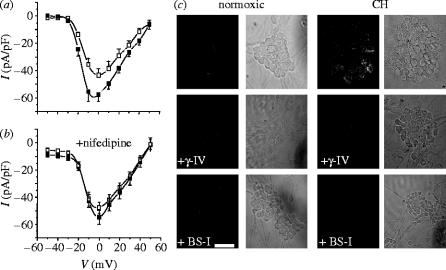
Figure 4.
Hypoxia augments voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in cerebellar granule neurons. (a) Mean (+s.e.m. bars) current density versus voltage relationships obtained from neurons cultured under normoxic (open squares; n=13 cells) or chronically hypoxic (solid squares; n=17 cells) conditions. (b) Mean (+s.e.m. bars) current density versus voltage relationships obtained from neurons cultured under normoxic (open squares; n=12 cells) and chronically hypoxic (solid squares; n=14 cells) conditions, and recorded in the presence throughout of 2 μM nimodipine. (c) Immunofluorescent images of clusters of cerebellar granule cell bodies (together with bright field images, to the right of each) cultured either normoxically (left) or under chronically hypoxic conditions (right) in the absence of secretase inhibitors (top row) or in the presence of the γ-secretase inhibitor γ-IV (3 μM; middle row) or the β-secretase inhibitor, BS-I (30 nM; bottom row). Scale bar shown in the bottom of the figure indicates 10 μm and applies to all panels.