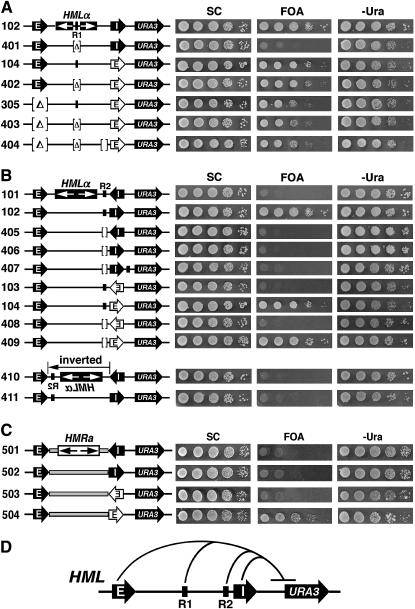
Figure 7.—
Multiple dispersed silencing elements can cooperate to promote silencing outside the region harboring them. (A) The protosilencer R1 within the HML sequence is involved in silencing outside of HML. Left, strains used. Right, growth phenotypes. (B) The Rap1p-binding site near HML-I in HML (designated R2) is involved in silencing outside of HML. Left, strains used. Strains 410 and 411 are identical with 101 and 102, respectively, except that the HML sequence bracketed by the HML-E and -I silencers is inverted. Note that R2 is highlighted only in certain relevant strains in this report. Right, growth phenotypes. (C) Effects of replacing the HML sequence with the HMR sequence on silencing outside of HML. The HMR sequence excluding the HMR silencers (coordinates 291,539–293,532 of chromosome III) indicated by shaded rectangles was used to replace the HML sequence excluding the HML silencers in strains 101–104, making strains 501–504. (D) Four dispersed silencing elements at HML synergize to promote silencing outside HML. The HML-E and inverted HML-I silencers as well as the R1 and R2 protosilencers were all required for the silencing of URA3 located to the right of HML. This is a summary of results concerning strains 102, 302, 303, 401, and 406 described in Figures 1 and 5–7.