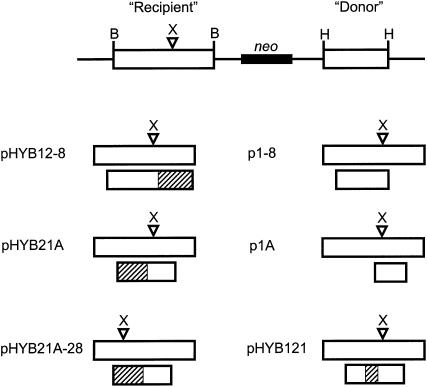
Figure 1.—
Recombination substrates. (Top) A schematic of a generic recombination substrate. The DNA construct is shown as if linearized at the unique ClaI site in the vector. Inserted between two BamHI sites (B) is a 2.5-kb fragment containing an HSV-1 tk gene disrupted by insertion of an XhoI (X) linker and referred to as a “recipient.” Inserted between two HindIII (H) sites is a truncated tk sequence referred to as a “donor.” The direction of transcription of recipient and donor tk sequences is from left to right, and the two tk sequences are separated by ∼4.4 kb. Below the generic substrate are schematics of the recipient and donor tk sequences contained in the six specific recombination substrates used. For each substrate, the recipient gene is shown on top with the donor gene aligned beneath it. Open rectangles represent HSV-1 tk sequences while stippled rectangles represent HSV-2 tk sequences. For pHYB21A-28 the recipient tk gene is mutant 28, while for all other substrates the recipient tk gene is mutant 8 (see materials and methods).