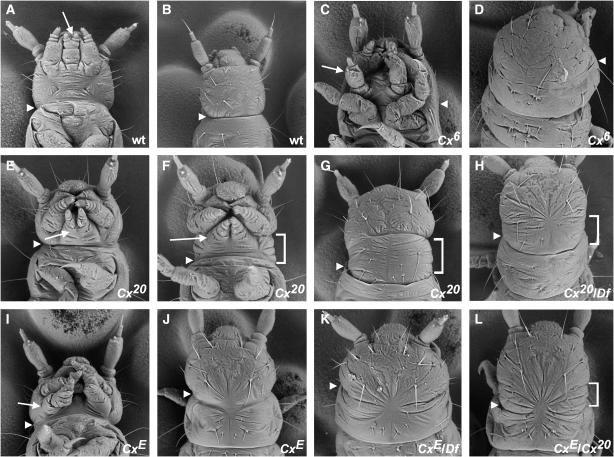
Figure 2.—
Scanning electron micrographs of wild-type and Cx mutant Tribolium larvae. The boundary between head and thorax (approximated in cephalized mutants) is denoted by an arrowhead in A–L, and the labial appendages are indicated by an arrow in all ventral views. (A) Wild type, ventral view. (B) Wild type, dorsal view. (C) Cx6 homozygote, ventral view. Note the transformation of labial appendages to antennae (arrow) and the fusion of T1 with the head. (D) Cx6 homozygote, dorsal view. T1 is fused with the head dorsally as well as ventrally. (E) Cx20 homozygote, ventral view. The phenotype of Cx20 homozygotes is variable. In this mildly affected individual, the labial appendages are more posteriorly located than in wild type and only the most proximal segment of each appendage is fused. The extra dorsal segment between the head and T1 is not visible from the ventral side. (F) Cx20 homozygote, ventral view. In a more severely affected individual, the labial appendages completely fail to fuse. The extra dorsal segment between the head and T1 (bracket) can be seen from the ventral side. (G) Cx20 homozygote, dorsal view. Note the extra segment (bracket) between the head and T1. (H) Cx20 hemizygote [Cx20/Df(HOMC)], dorsal view. An extra segment (bracket) is present, although partly obscured by dorsal closure defects. (I) CxE homozygote, ventral view. The labial appendages are positioned laterally, in a similar orientation to the maxillary appendages. Note the triangular head shape. (J) CxE homozygote, dorsal view. A segmental groove is present between the head and thorax, but does not appear as deep as in wild type. (K) CxE hemizygote [CxE/Df(HOMC)], dorsal view. T1 is fused with the head. The head has the abnormal triangular shape seen in CxE homozygotes. (L) CxE/Cx20, dorsal view. An extra segment is present (bracket) although not as distinct as in Cx20 homozygotes. Head shape is apparently normal.