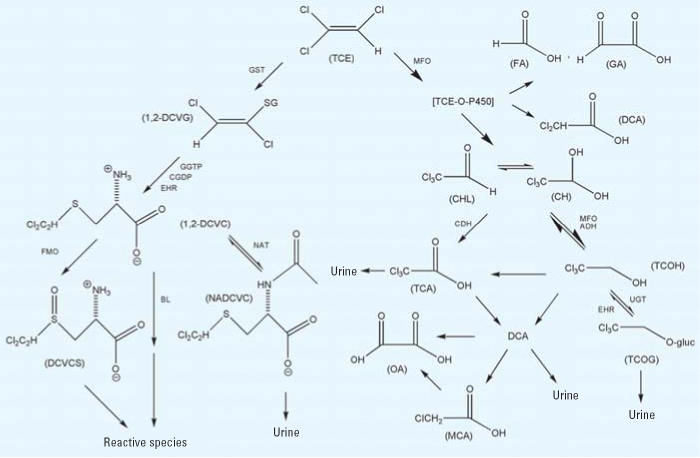
Figure 1.
Postulated metabolism scheme for trichloroethylene. Figure adapted from Clewell et al. (2000) and Lash et al. (2000a). For the GSH pathway, metabolism to 1,2-DCVG is shown, but 1,1-DCVG goes through similar steps through 1,1-DCVC to N-acetylated and reactive species.
Abbreviations: ADH, alcohol dehydrogenase; BL, cysteine conjugate β-lyase; CDH, chloral dehydrogenase (aldehyde oxidase); CGDP, cysteinyl-glycine dipeptidase; CH, chloral hydrate; CHL, chloral; DCA, dichloroacetic acid; DCVC, S-dichlorovinyl-l-cysteine; DCVCS, 1,2-DCVC sulfoxide; DCVG, S-dichlorovinyl glutathione; EHR, enterohepatic recirculation; FA, formic acid; FMO, flavin-containing monooxygenase; GA, glyoxylic acid; GGTP, γ-glutamyl transpeptidase; GST, glutathione S-transferase; MCA, monochloroacetic acid; MFO, mixed-function oxidase (i.e., cytochrome P450); NAT, N-acetyltransferase; NADCVC, N-acetyl-1,2-DCVC; OA, oxalic acid; TCE-O-P450, oxygenated TCE-cytochrome P450 transition state complex; TCA, trichloroacetic acid; TCOG, trichloroethanol glucuronide; TCOH, trichloroethanol; UGT, uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase.