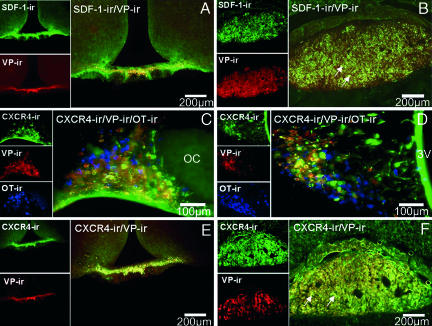
Fig. 1.
Colocalization of SDF-1 and CXCR4 receptor immunoreactivity (ir) with AVP (VP) in the hypothalamus and posterior pituitary in the rat. (A and B) Double immunohistochemistry of SDF-1 (stained in green) with AVP (stained in red) in the median eminence (A) and in the posterior pituitary (B). Simple stainings are presented in the small pictures of each panel. In the median eminence, SDF-1 strictly colocalizes with the AVP processes in the internal zone. In the pituitary, a strong SDF-1 immunostaining is observed in the posterior lobe of the pituitary, which is similar to the localization of AVP nerve terminals in this region, in particular in the probable Herring bodies (arrows). (Scale bars, 200 μm.) (C and D) Triple immunohistochemistry of CXCR4 (stained in green) with AVP (stained in red) and OT-expressing neurons (stained in blue) in the SON (C) and PVN (D). Eighty-five percent and 95% of the AVP neurons colocalize with CXCR4 immunoreactivity in the SON and PVN, respectively. No colocalization is observed between OT-positive neurons and CXCR4 immunostaining. Simple stainings are presented in the small pictures of each panel. (Scale bars, 100 μm.) (E and F) Double immunohistochemistry of CXCR4 (stained in green) with AVP (stained in red) in the median eminence (E) and in the posterior pituitary (F). Simple stainings are presented in the small pictures of each panel. (Scale bars, 200 μm.) In the median eminence, CXCR4 strictly colocalizes with the AVP processes in the internal zone. In the pituitary, a strong CXCR4 immunostaining is observed in the posterior lobe of the pituitary, which is similar to the localization of AVP nerve terminals in this region, in particular in the probable Herring bodies (arrows). All sections were observed with a fluorescence microscope (BX61; Olympus, Melville, NY), and images were computed for quantitative analysis.