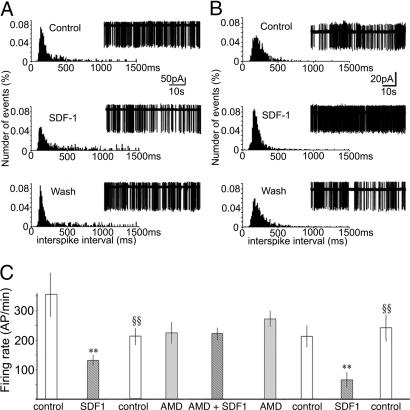
Fig. 2.
Electrophysiological characterization of the effect of SDF-1 on the action-potential firing pattern of AVP neurons in SON. Modulation by SDF-1 of action-potential firing in magnocellular neurosecretory cells is shown, as are typical normalized distribution histograms of the interspike intervals (ISIs) (left sides) of action potentials (right sides) recorded before, during, and after perfusion of 25 nM SDF-1 in different neurons. (A) SDF-1 inhibits the activity of AVP and decreases the duration of active periods. (B) SDF-1 stimulates the activity of AVP neurons and blunts the silent periods. (C) Sequence of a typical experimental protocol used to study the effect of SDF-1 and the implication of CXCR4. The number of action potentials per minute (AP/min) was recorded during 5-min periods under the conditions indicated. Note that the inhibitory effect of SDF-1 on action potentials is reproducible and reversibly inhibited by 10 μM AMD. Results are expressed as the means ± SEM. ∗∗, P < 0.01 vs. respective controls; §§, P < 0.01 vs. SDF-1.