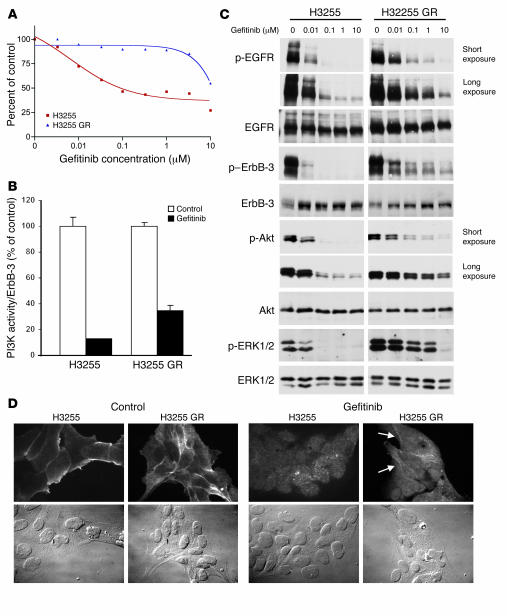
Figure 1. Generation of a cell line, H3255 GR, with acquired resistance to gefitinib.
(A) H3255 and H3255 GR cell lines were subjected to MTS survival assays in increasing concentrations of gefitinib (see Methods). (B) ErbB-3 was immunoprecipitated from H3255 and H3255 GR cells grown with or without 1 μM gefitinib for 6 hours. Half of the immunoprecipitate was used for ErbB-3 quantification; the other half was used for PI3K assays (see Methods). PI3K activity normalized to ErbB-3 protein is shown as a percent of control (no gefitinib). (C) H3255 and H3255 GR cells were exposed to increasing amounts of gefitinib for 24 hours prior to lysis. Blots of H3255 and H3255 GR extracts for each antibody are the same exposure from a single gel and blot; an irrelevant lane between the H3255 and H3255 GR extracts was omitted. (D) H3255 and H3255 GR cells were serum-starved overnight followed by treatment with or without 1 μM gefitinib for 3 hours followed by stimulation with EGF. Immunofluorescence was performed using anti–p-EGFR (pY1068) antibodies. Left: p-EGFR membrane staining by immunofluorescence in untreated H3255 and H3255 GR cells and corresponding phase-contrast images (bottom panels). Right: Immunofluorescence and phase-contrast images of H3255 and H3255 GR cells treated with gefitinib. Most H3255 GR cells maintained detectable membrane EGFR staining in the presence of gefitinib (arrows). The gefitinib-treated panels were equally overexposed to highlight the residual membrane staining. Magnification, ×60.