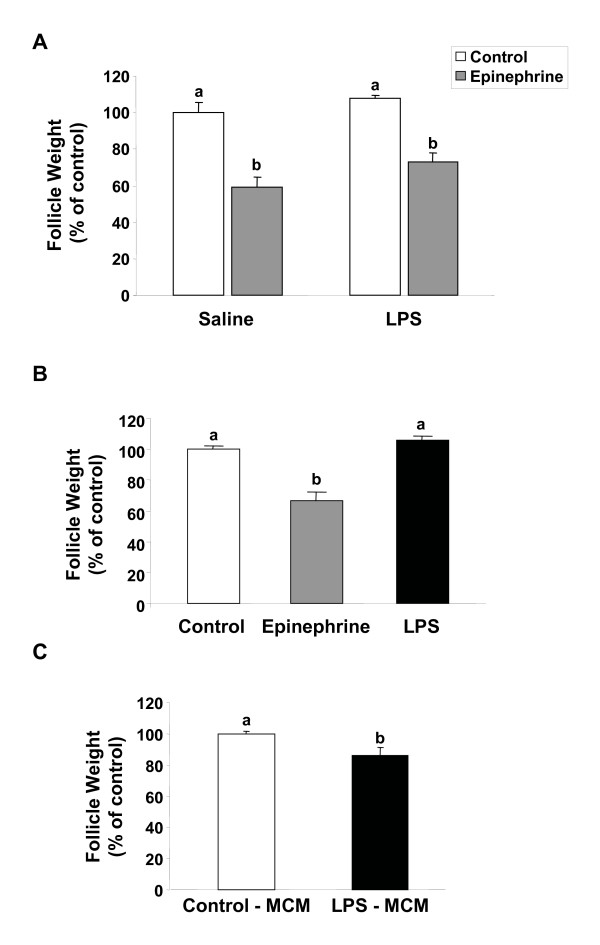
Figure 5.
Effects of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) on follicular contraction in brook trout. A. Effects of in vivo LPS administration on trout follicular contraction. Punctured, preovulatory brook trout follicles from saline- and LPS-treated fish were incubated for 8 h at 12°C in the absence or presence of epinephrine (5μM). Each bar represents the mean ± SEM of five fish for each treatment, with each assayed in triplicate. The results are expressed as percent change with respect to the saline-injected control (no epinephrine) group which has been set at 100%. Statistically significant (p ≤ 0.0001) differences among groups are indicated by different letters. B. Effects of LPS treatment in vitro on trout follicular contraction. Punctured trout preovulatory ovarian follicles were incubated in the absence or presence of epinephrine (5μM) or LPS (25 μg/ml) for 8 hours. The results show the mean ± SEM from six separate experiments, with each assayed in triplicate. Statistically significant (p ≤ 0.001) differences among groups are indicated by different letters. C. Effects of macrophage conditioned medium on trout follicular contraction. Punctured, trout ovarian follicles were incubated with macrophage conditioned medium (Control-MCM) and with LPS-stimulated macrophage-conditioned medium (LPS-MCM) for 8 hours. Statistically significant (p < 0.05) differences among groups are indicated by different letters.