Figure 2.
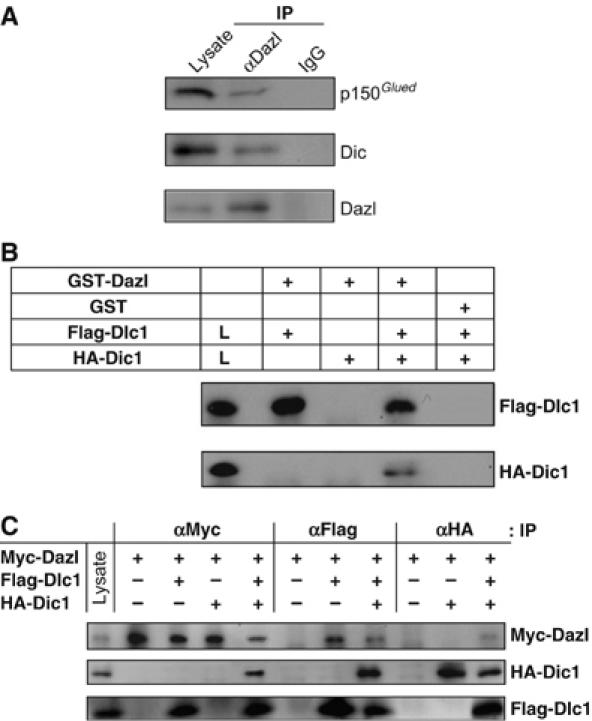
Association of Dazl with the dynein–dynactin complex. (A) In vivo interaction of Dazl with Dic and p150Glued in the testis. The endogenous Dazl protein in the testicular lysates was immunoprecipitated (IP), and the coimmunoprecipitated proteins were detected using the specific antibodies against p150Glued and Dic. IgG was used as a control for immunoprecipitation. Testicular lysates were used for detection of the endogenous p150Glued, Dic and Dazl proteins in the immunoblots. (B) Indirect interaction of Dazl with Dic: GST pull-down assay. The 293T cell lysates transfected with pFlag-Dlc1 and/or pHA-Dic1 were incubated with the GST-Dazl fusion protein or with the GST protein as a control. The precipitated Dlc1 and Dic1 proteins were detected using the Flag and HA antibodies, respectively. The HA-Dic1 protein was precipitated with GST-Dazl only in the presence of Flag-Dlc1. (C) Indirect interaction of Dazl with Dic: immunoprecipitation assay. The 293T cell lysates cotransfected with pFlag-Dlc1 and/or pHA-Dic1 along with the Dazl expression vector (pMyc-Dazl) were immunoprecipitated, followed by immunoblotting using the indicated antibodies. The cell lysates were loaded on the gels to confirm the expression of Myc-Dazl, HA-Dic1 and Flag-Dlc1 proteins in the cells. The HA-Dic1 protein was coimmunoprecipitated with Myc-Dazl only in the presence of Flag-Dlc1.
