Figure 2.
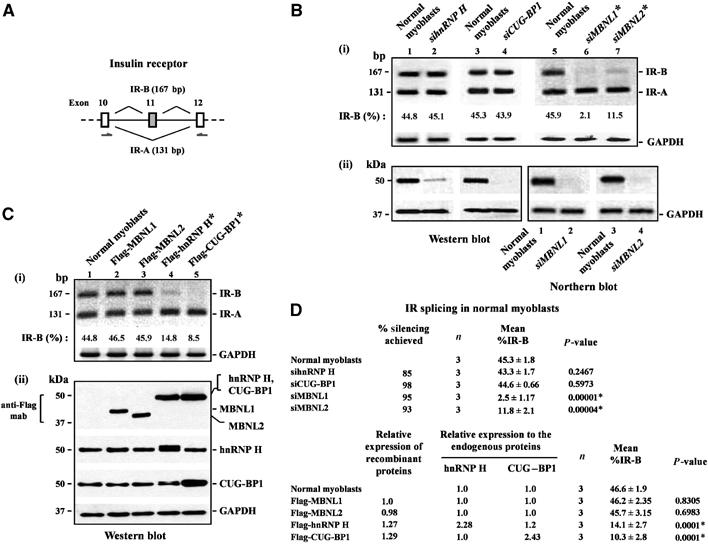
Overexpression of hnRNP H induces abnormal IR splicing in normal human myoblasts. (A) Schematic of the IR genomic sequence encoding exons 10, 11 and 12 is shown. Primers used to amplify the IR-B (167 nt; exon 11 is included) and the IR-A (131 nt; exon 11 is excluded) isoforms are indicated. (B) siRNA-mediated downregulation of hnRNP H does not alter IR splicing in normal myoblasts. Normal myoblasts were transfected with siRNAs directed against hnRNP H, CUG-BP1, MBNL1 and MBNL2, and total RNA was isolated 5 days after transfection and subjected to RT–PCR analysis using IR primers indicated. IR-B and IR-A levels were measured by densitometry analyses and % IR-B was calculated as described in Materials and methods. Levels of IR-B obtained in the experiment shown in (i) are indicated. (ii) siRNA-mediated silencing was studied by analyzing of 10 μg of protein by Western blot analyses for hnRNP H and CUG-BP1. 1.0 μg of mRNA was subjected to Northern blot analyses to measure the silencing achieved for MBNL1 and MBNL2. (C) Overexpression of Flag-hnRNP H results in decreased IR exon 11 splicing. Normal myoblasts were transfected with Flag tagged-MBNL1, MBNL2, hnRNP H and CUG-BP1, and total RNA was isolated 48 h later and subjected to RT–PCR analyses using IR primers as indicated. Levels of IR-B obtained in the experiment shown in (i) are indicated. (ii) Total protein (10 μg) was analyzed by Western blots to measure the relative expression of MBNL1, MBNL2, hnRNP H and CUG-BP1 using the anti-Flag, anti-hnRNP H and anti-CUG-BP1 antibodies, respectively. The blots were stripped and re-probed for GAPDH protein (Western blot) or GAPDH mRNA (Northern blot) expression as an internal control. For the RT–PCR analyses, GAPDH RNA was amplified as an internal control. (D) The results of three independent experiments of altered hnRNP H, CUG-BP1, MBNL1 and MBNL2 dosage on IR exon 11 splicing in normal myoblasts are tabulated. The asterisk (*) represents significant differences from the control (Student's two-tailed t-test; P<0.05).
